That would be interesting, I agree. Assuming there is such a thing. Again, I will stick to my refusal to read papers and sail on in my ignorance, and claim that no one really knows properties of anything at the extremes where g is close to that at an event horizon (incidentally, what is that value in m/s^2, please?) or even close to a neutron star level. And there MUST be something on the 'other side', i.e., superlumic. Way too much is being assumed about internals of black holes etc. That argument about the dumbbells inside the pregnant star was just way way "out there" in showing what happens when incomplete theory is extrapolated.deduce properties of neutronium
Physics Discussion Thread
-
UlanBatori
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 14045
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
Re: Physics Thread.
I fail to understand why something I added is considered "corrected" (and if there is some thing wrong why not correct it anyway instead of getting irritated) but this does not matter...last from me here in this dhaga....Obviously I mis-judged the audience but I wish you all well .. and of course..A_Gupta wrote: I also now see why people get irritated with our resident recognized and respected physicist. Nothing that I wrote was wrong, but was pedantically "corrected" anyway. Bye-bye from this thread!
UlanBatori wrote: P.S. Pls send NoBill Price to Ulan Batori, PO Box1313666, Gujranwala PO, Bakistan onlee.
Re: Physics Thread.
See, no one has been inside the sun, so anyone can talk anything about it and make up theories. How do we know which theory is right and which is wrong? If the theory shows major inconsistencies, then its a wrong theory.NRao wrote:Is someone saying it takes that long to travel within the Sun? Is it due to the density or because the photons do/can not travel in a straight line?Yea, apparantly, light takes more time to travel lesser distance. It seems that a photon takes 4000 years to travel the lesser distance and 8 minutes to travel 215 times more distance. Woah! If this is not nonsense, I don't know what is.
Also, the 4000 years must be an average? So, a photon could zip in the fast lane and take a few years, while some could take eons. All ave 4000?
The inconsistency in the behaviour of Photons:
Inside the sun:
photons don't travel straight like a drunk man.
photons take extremely long time to cover the distance. Infact, their speed is 0.0055 m/s. That means photons are traveling slower than the walking speed. People could walk across sun faster than a photon.
Outside the sun:
photons travel in straight lines. Their bending is a rare phenomenon. Photons take the shortest route.
photons travel extremely fast. Infact, they are the fastest of all elements. We can't cross the barrier of speed of light regardless of what machine or mechanism we use.
The inconsistency in this theory in the behaviour of the same photon inside the sun and outside the sun, is quite clear.
No, that doesn't help. Sugar in unstirred coffee doesn't start flying away in great speeds.A_Gupta wrote:Yours truly was a physicist. The Sun's interior is a dense plasma - i.e., a soup of charged particles that interacts readily with photons. As the homework solution points out initially, the mean free path of the photon in that environment is of the order of 10^-5 meters. Which means it propagates on the average that distance, before suffering a collision and shooting off in another random direction. It is essentially diffusing through the medium, like sugar in your unstirred coffee.
Hope that helps.
So, what accelerates the photon to a speed of 300,000,000 m/s outside the sun from around a speed of 0.0055 m/s inside the sun? So something is accelerating the photon at the surface of the sun according to your theory, what is it? Is it all because of the density of the sun(plasma according to you)?
Re: Physics Thread.
There is a huge difference between "Yes, and ...." and "No, but .....".
Re: Physics Thread.
You didn't answer the question: What accelerates the photon from 0.0055 m/s to 300,000,000 m/s at the surface of the sun?
Re: Physics Thread.
A_gupta: neutronium? Sounds like a new element. But then you could be one of those physicists who impressed a few mighty Nobel laureates (Ref: soc.culture.indian and caltech).
Last edited by Vayutuvan on 24 Feb 2016 07:02, edited 1 time in total.
Re: Physics Thread.
I didn't understand your point. Space-time is a continuum in Einstein system. There are no discontinuities as far as I understand.vayu tuvan wrote:johneeG: Your argument does not stand. You are assuming that the domain is continuous. It is not once it falls below a certain distance scale. For example spin is quantized.
Linkwiki wrote:In general relativity, spacetime is assumed to be smooth and continuous—and not just in the mathematical sense. In the theory of quantum mechanics, there is an inherent discreteness present in physics. In attempting to reconcile these two theories, it is sometimes postulated that spacetime should be quantized at the very smallest scales. Current theory is focused on the nature of spacetime at the Planck scale. Causal sets, loop quantum gravity, string theory, causal dynamical triangulation, and black hole thermodynamics all predict a quantized spacetime with agreement on the order of magnitude. Loop quantum gravity makes precise predictions about the geometry of spacetime at the Planck scale.
Spin networks provide a language to describe quantum geometry of space. Spin foam does the same job on spacetime. A spin network is a one-dimensional graph, together with labels on its vertices and edges which encodes aspects of a spatial geometry.
Re: Physics Thread.
JohneeG: it is not known whether time is quantized. Do You know about spin glasses, Ising models? Lattice gas? All are discrete models of what physicists think is reality.
Re: Physics Thread.
I think you are talking about quantum mechanics which is a totally different field and unrelated to this as far as I understand.vayu tuvan wrote:JohneeG: it is not known whether time is quantized. Do You know about spin glasses, Ising models? Lattice gas? All are discrete models of what physicists think is reality.
Re: Physics Thread.
because the photons never stopped going at the speed of light, they are traveling through denser material and being deflected at different angles, still at the speed of light. when they finally emerge they are going at their usual speed of light but now through a vacuum. yeehaw, giddy up......johneeG wrote:You didn't answer the question: What accelerates the photon from 0.0055 m/s to 300,000,000 m/s at the surface of the sun?
no thanks necessary, just my usual and customary fee.......
Re: Physics Thread.
may be it is particle only in a denser medium and a wave when there are no blockers. like the motor bike riders in Indian roads. 
ps: doesn't that mean c is not constant?
where is our resident fizzic guru - bade?
ps: doesn't that mean c is not constant?
where is our resident fizzic guru - bade?
Re: Physics Thread.
TSJones wrote:because the photons never stopped going at the speed of light, they are traveling through denser material and being deflected at different angles, still at the speed of light. when they finally emerge they are going at their usual speed of light but now through a vacuum. yeehaw, giddy up......johneeG wrote:You didn't answer the question: What accelerates the photon from 0.0055 m/s to 300,000,000 m/s at the surface of the sun?
no thanks necessary, just my usual and customary fee.......
Ok, so its density. Alright, speed of light in a medium is dependent on density of the medium.SaiK wrote:may be it is particle only in a denser medium and a wave when there are no blockers. like the motor bike riders in Indian roads.
ps: doesn't that mean c is not constant?
where is our resident fizzic guru - bade?
LinkIn optics, the refractive index or index of refraction n of a material is a dimensionless number that describes how light propagates through that medium. It is defined as
refractive index(which is based on density) = speed of light in vacuum/ speed of light in the medium.
So, here is a list of refractive indices:
vacuum(density -0) - refractive index -1.
air - 1.0001.
water - 1.333
ice(0.9 gm/cm3) - 1.3
glass - 1.5
diamond (4 gm/cm3) - 2.5
Notice that the refractive index does not even cross 5.
Now, what is the refractive index of the sun based on these speeds = 300,000,000/0.0055 = 3 * 10^12.
Compare the refractive index of 5 vs 3*10^12.
diamond has 2.5 refractive index and a density of 4 gm/cm3.
so, what would sun's density be with 3*10^12 refractive index?
2.5(refractive index of diamond) -> 4(known density of diamond)
3*10^12(refractive index of sun) -> x(unknown density of sun)
2.5*x = (3*10^12)*4
x = 4.8 * 10^12
x = 4800000000000 gm/cm3 (approximate density of sun)
x = 4800000000 kg/cm3 (approximate density of sun)
x = 4800000 Tons/cm3 (approximate density of sun)
So, the sun has an approximate density of 4800000 Tons per cm3 for it to have photons traveling at a speed of 0.0055 m/s for 4000 years. Now, the densest element in universe supposedly has a density of around: 22.5 g/cm3. Its supposedly Osmium. So, compare 22.5 gm/cm3 & 4800000000000 g/cm3.
-
UlanBatori
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 14045
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
Value of g at Event Horizon pls? This must be a universal constant, hain?
-
member_22733
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 3788
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
Take a thick walled pipe made with lead, pass molten iron through it for a second. Once the iron has exited how long did it take the lead pipe to get back to normal temperature?
That is how long energy, as photons, takes to get from the inside of the pipe to the outside.
That is how long energy, as photons, takes to get from the inside of the pipe to the outside.
-
member_22733
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 3788
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
In which frame of reference? For an outside observer, its 0 since they will never see anything cross the event horizon due to time dilation.UlanBatori wrote:Value of g at Event Horizon pls? This mus be a universal constant, hain?
Re: Physics Thread.
Iron and lead are not transparent, so light does not pass through them. But, Lead & Iron are a good conductor of heat and electricity, so energy travels very fast through iron & lead. Lead has a density of 11 g/cm3 & Iron has a density of 7 g/cm3. Sun's density must be so much much higher(around tons/cm3) if the photons have to stay there for 4000 years. But, the most densest element is supposed to be just 22 g/cm3. So, the numbers don't add up. Its just not possible for a photon to stay for 4000 years in the sun and suddenly travel so much faster outside the sun.
----
UB saar,
By definition of Black hole, gravity is supposed to be infinity. But, now, they are trying to give it a new spin from the time of Hawking radiation.
----
UB saar,
By definition of Black hole, gravity is supposed to be infinity. But, now, they are trying to give it a new spin from the time of Hawking radiation.
-
member_22733
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 3788
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
The sun is not transparent. It's an almost ideal black body.
Re: Physics Thread.
If sun is an ideal black body, then the sun light would not have escaped sun.LokeshC wrote:The sun is not transparent. It's an almost ideal black body.
-
member_22733
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 3788
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
Re: Physics Thread.
Black body only absorbs or emits energy. It doesn't produce energy. So, if sun were a black body, then there won't be any sun light produced.LokeshC wrote:If what you say is true, a guy called Max Planck could not have discovered the possibility of the world being Quantum Mechanical.
And blackbody properties were determined by Planck in Thermal Equilibrium conditions. Is their thermal equilibrium in and around sun?
Re: Physics Thread.
Here is what they say about 'perfect blackbodies':
So, perfect black bodies don't allow light to re-emerge, isn't it? Only heat is emitted, isn't it? Planck's law is about thermodynamics(i.e. related to heat), right?
Kirchhoff's perfect black bodies
Kirchhoff in 1860 introduced the theoretical concept of a perfect black body with a completely absorbing surface layer of infinitely small thickness, but Planck noted some severe restrictions upon this idea. Planck noted three requirements upon a black body: the body must (i) allow radiation to enter but not reflect; (ii) possess a minimum thickness adequate to absorb the incident radiation and prevent its re-emission; (iii) satisfy severe limitations upon scattering to prevent radiation from entering and bouncing back out. As a consequence, Kirchhoff's perfect black bodies that absorb all the radiation that falls on them cannot be realized in an infinitely thin surface layer, and impose conditions upon scattering of the light within the black body that are difficult to satisfy.
LinkAn approximate realization of a black surface is a hole in the wall of a large enclosure (see below). Any light entering the hole is reflected indefinitely or absorbed inside and is unlikely to re-emerge, making the hole a nearly perfect absorber. The radiation confined in such an enclosure may or may not be in thermal equilibrium, depending upon the nature of the walls and the other contents of the enclosure.
So, perfect black bodies don't allow light to re-emerge, isn't it? Only heat is emitted, isn't it? Planck's law is about thermodynamics(i.e. related to heat), right?
Re: Physics Thread.
the sun's surface temp is 6000 degrees. that is white hot.
the electromagnetic spectrum in the form of gamma rays heat the sun's surface to a white hot temp.
that is what is visible to us.
the electromagnetic spectrum in the form of gamma rays heat the sun's surface to a white hot temp.
that is what is visible to us.
Re: Physics Thread.
I am completely lost! Never mind.
Re: Physics Thread.
me too. I thought I got the numbers, but just like photons around sun, my neurons are hitting denser materials in my mind. we are now going black & white for many day and night now.  can someone summarize in laid-back terms?
can someone summarize in laid-back terms?
Re: Physics Thread.
wiki sayeth thusly:
In astronomy, the radiation from stars and planets is sometimes characterized in terms of an effective temperature, the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total flux of electromagnetic energy.
The effective temperature of the Sun (5777 K) is the temperature a black body of the same size must have to yield the same total emissive power.
The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per surface area (\mathcal{F}_{\rm Bol}) as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law \mathcal{F}_{\rm Bol}=\sigma T_{\rm eff}^4. Notice that the total (bolometric) luminosity of a star is then L=4 \pi R^2 \sigma T_{\rm eff}^4, where R is the stellar radius.[2] The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightforward. More rigorously the effective temperature corresponds to the temperature at the radius that is defined by a certain value of the Rosseland optical depth (usually 1).[3][4] The effective temperature and the bolometric luminosity are the two fundamental physical parameters needed to place a star on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Both effective temperature and bolometric luminosity actually depend on the chemical composition of a star.
The effective temperature of our Sun is around 5780 kelvin (K).[5][6] Stars actually have a temperature gradient, going from their central core up to the atmosphere. The "core temperature" of the sun—the temperature at the centre of the sun where nuclear reactions take place—is estimated to be 15 000 000 K.
The color index of a star indicates its temperature from the very cool—by stellar standards, that is—red M stars that radiate heavily in the infrared to the very blue O stars that radiate largely in the ultraviolet. The effective temperature of a star indicates the amount of heat that the star radiates per unit of surface area. From the warmest surfaces to the coolest is the sequence of star types known as O, B, A, F, G, K, and M.
A red star could be a tiny red dwarf, a star of feeble energy production and a small surface or a bloated giant or even supergiant star such as Antares or Betelgeuse, either of which generates far greater energy but passes it through a surface so large that the star radiates little per unit of surface area. A star near the middle of the spectrum, such as the modest Sun or the giant Capella radiates more heat per unit of surface area than the feeble red dwarf stars or the bloated supergiants, but much less than such a white or blue star as Vega or Rigel.
In astronomy, the radiation from stars and planets is sometimes characterized in terms of an effective temperature, the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total flux of electromagnetic energy.
The effective temperature of the Sun (5777 K) is the temperature a black body of the same size must have to yield the same total emissive power.
The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per surface area (\mathcal{F}_{\rm Bol}) as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law \mathcal{F}_{\rm Bol}=\sigma T_{\rm eff}^4. Notice that the total (bolometric) luminosity of a star is then L=4 \pi R^2 \sigma T_{\rm eff}^4, where R is the stellar radius.[2] The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightforward. More rigorously the effective temperature corresponds to the temperature at the radius that is defined by a certain value of the Rosseland optical depth (usually 1).[3][4] The effective temperature and the bolometric luminosity are the two fundamental physical parameters needed to place a star on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram. Both effective temperature and bolometric luminosity actually depend on the chemical composition of a star.
The effective temperature of our Sun is around 5780 kelvin (K).[5][6] Stars actually have a temperature gradient, going from their central core up to the atmosphere. The "core temperature" of the sun—the temperature at the centre of the sun where nuclear reactions take place—is estimated to be 15 000 000 K.
The color index of a star indicates its temperature from the very cool—by stellar standards, that is—red M stars that radiate heavily in the infrared to the very blue O stars that radiate largely in the ultraviolet. The effective temperature of a star indicates the amount of heat that the star radiates per unit of surface area. From the warmest surfaces to the coolest is the sequence of star types known as O, B, A, F, G, K, and M.
A red star could be a tiny red dwarf, a star of feeble energy production and a small surface or a bloated giant or even supergiant star such as Antares or Betelgeuse, either of which generates far greater energy but passes it through a surface so large that the star radiates little per unit of surface area. A star near the middle of the spectrum, such as the modest Sun or the giant Capella radiates more heat per unit of surface area than the feeble red dwarf stars or the bloated supergiants, but much less than such a white or blue star as Vega or Rigel.
Re: Physics Thread.
WTF!
These phjicks geeks.
It ij either Jeero or Inphinity for black holes
These phjicks geeks.
It ij either Jeero or Inphinity for black holes
-
Mort Walker
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 10040
- Joined: 31 May 2004 11:31
- Location: The rings around Uranus.
Re: Physics Thread.
There is too much confusion in this thread. If AmberG can please come back and straighten this out it will certainly help.
Just to make it clear. Our sun is not a perfect black body, but an ideal reference black body since it is consistent and predictable.
Just to make it clear. Our sun is not a perfect black body, but an ideal reference black body since it is consistent and predictable.
Re: Physics Thread.
I personally think that talking about sun is just speculation. But, the point I am trying to make is that the numbers don't add up and theories don't make sense.
These are mainstream numbers:
mass of sun - 2* 10^30 * 10^3 g
radius of sun - 696,000 * 10^5 cm
volume of sun(sphere) - (4/3)*pi(r^3) = (4/3)*(pi)*( (696,000*10^5 cm)^3) = 1.4122654291058958451420952274396 & 10^33 cm^3
density of sun = mass/volume = (2* 10^30 * 10^3 )g / 1.4122654291058958451420952274396 & 10^33 cm^3
density of sun = 1.4161643829702738378121334314511 g/cm^3 = 1.4 g/cm^3
Density of water is around 1 g/cm^3 and density of glass is 2.5 g/cm^3. So, density of sun is more than water and less than density of glass. Since, refractive index(the relative speed of light in a medium) is related to density, refractive index of sun must be between the refractive indices of water & glass. Refractive index of water is 1.3. Refractive index of glass is 1.5. So, refractive index of sun must be somewhere between 1.3 to 1.5. Ok, even if we allow some leeway(ok, lets allow plenty of leeway), then refractive index should be somewhere around 1 to 10. It should not be 3*10^12 i.e. take 4000 years for photons to travel a distance of 696,000 km.
These are mainstream numbers:
mass of sun - 2* 10^30 * 10^3 g
radius of sun - 696,000 * 10^5 cm
volume of sun(sphere) - (4/3)*pi(r^3) = (4/3)*(pi)*( (696,000*10^5 cm)^3) = 1.4122654291058958451420952274396 & 10^33 cm^3
density of sun = mass/volume = (2* 10^30 * 10^3 )g / 1.4122654291058958451420952274396 & 10^33 cm^3
density of sun = 1.4161643829702738378121334314511 g/cm^3 = 1.4 g/cm^3
Density of water is around 1 g/cm^3 and density of glass is 2.5 g/cm^3. So, density of sun is more than water and less than density of glass. Since, refractive index(the relative speed of light in a medium) is related to density, refractive index of sun must be between the refractive indices of water & glass. Refractive index of water is 1.3. Refractive index of glass is 1.5. So, refractive index of sun must be somewhere between 1.3 to 1.5. Ok, even if we allow some leeway(ok, lets allow plenty of leeway), then refractive index should be somewhere around 1 to 10. It should not be 3*10^12 i.e. take 4000 years for photons to travel a distance of 696,000 km.
Re: Physics Thread.
Density of water 1 gm/cm^3, I thought.
Re: Physics Thread.
Strictly speaking, its not even infinity. It is division by zero. In normal maths, division by zero is undefined. Only in calculus, they use the concept of 'approaching zero but not actually zero' i.e. division by 0.0000000000000001.Gagan wrote:WTF!
These phjicks geeks.
It ij either Jeero or Inphinity for black holes
Now, as a mathematical concept, it may make sense. But, as a physical concept it makes no difference whether its 0 or 0.0000000000000001. It is effectively zero from a physical sense.
It was a typo. Corrected it before your post.saip wrote:Density of water 1 gm/cm^3, I thought.
Re: Physics Thread.
......the sun is not uniformly dense through out it's volume. that is an accepted fact by scientists who understand fusion. therefore the speed of the gamma rays are not uniform inside the sun as they travel through various densities.
enjoy.......
correction: the gamma rays are going the speed of light but they are being randomly deflected at different intervals as they travel through different densities. va va voom.....
I remain TSJ, street warrior for Einstein......
enjoy.......
correction: the gamma rays are going the speed of light but they are being randomly deflected at different intervals as they travel through different densities. va va voom.....
I remain TSJ, street warrior for Einstein......
-
Bade
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 7212
- Joined: 23 May 2002 11:31
- Location: badenberg in US administered part of America
Re: Physics Thread.
refractive index also depends on the wavelength of light. Check wiki if you want to read more. For Gamma rays you are looking at very small wavelengths. The refractive index shoots up even at < 0.4 micron as shown below.refractive index of sun must be between the refractive indices of water & glass.
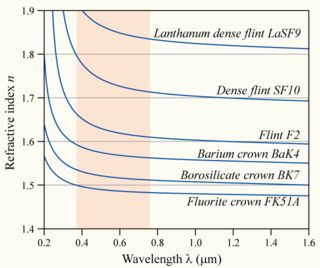
Gamma rays typically have frequencies above 10 exahertz (or >1019 Hz), and therefore have energies above 100 keV and wavelengths less than 10 picometers (10^−11 meter)
Re: Physics Thread.
As far as I understand, Blackbody mainly radiates heat. Sun mainly radiates light. So, how can the two be compared?Mort Walker wrote:There is too much confusion in this thread. If AmberG can please come back and straighten this out it will certainly help.
Just to make it clear. Our sun is not a perfect black body, but an ideal reference black body since it is consistent and predictable.
Facts should be independently verifiable. Anything beyond that is just opinions. Scientists can have their opinions. But, that should not be confused with facts.TSJones wrote:......the sun is not uniformly dense through out it's volume. that is an accepted fact by scientists who understand fusion. therefore the speed of the gamma rays are not uniform inside the sun as they travel through various densities.
enjoy.......
correction: the gamma rays are going the speed of light but they are being randomly deflected at different intervals as they travel through different densities. va va voom.....
I remain TSJ, street warrior for Einstein......
Now, this particular theory(opinion) that sun has non-uniform density is not even logical because I had read that Sun has thermal equilibrium(i.e. uniform temperature). If it has same temperature, then one would expect it to have same density through out. If it has different densities, then one would expect it to have different temperatures(that means no thermal equilibrium).
Anyway, in my earlier calculations, I actually gave benefit of doubt to the 4000 yr photon theory and assumed the density of sun to be uniformly high. Even then, the sun's density has to be around 1000s of tons per cm^3 for it to be possible. Such kind of density is not possible.
As for Einstein, he didn't believe in black holes and quantum mechanics.
-
member_22733
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 3788
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
JohneeG garu, do you know that heat is radiated as em waves? The reason we can "feel" heat is because our molecules interact with the infrared region of the spectrum. They also interact with higher frequency radiation such as UV and cause cancers radiation burn etc.
Radiation of thermal energy almost always is in the form of EM waves, AFAIK.
Radiation of thermal energy almost always is in the form of EM waves, AFAIK.
Re: Physics Thread.
Yes, but I read another theory also(or maybe I am making a mistake) that heat is due to the vibration of molecules. The more vibration means more heat or something of that sort. Thats why vacuum does not transmit heat. Vacuum flasks work on this principle. So, its said that sun only radiates only light and that light generates heat only when it enters Earth's atmosphere.LokeshC wrote:JohneeG garu, do you know that heat is radiated as em waves? The reason we can "feel" heat is because our molecules interact with the infrared region of the spectrum. They also interact with higher frequency radiation such as UV and cause cancers radiation burn etc.
Radiation of thermal energy almost always is in the form of EM waves, AFAIK.
Now, if heat is just infra-red radiation, then why doesn't vacuum transmit it? Vacuum does not stop other frequencies of light.
It seems there are more contradictions in these theories than I realized.
-
member_22733
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 3788
- Joined: 11 Aug 2016 06:14
Re: Physics Thread.
Vacuum transmits heat.  . Time to move to GDF phijjiks dhaaga???
. Time to move to GDF phijjiks dhaaga???
Heat transfer occur through conduction, convection AND radiation(as in EM radiation)
Heat transfer occur through conduction, convection AND radiation(as in EM radiation)
Re: Physics Thread.
Refractive index does not change due to wave-length:Bade wrote:refractive index also depends on the wavelength of light. Check wiki if you want to read more. For Gamma rays you are looking at very small wavelengths. The refractive index shoots up even at < 0.4 micron as shown below.refractive index of sun must be between the refractive indices of water & glass.
 Gamma rays typically have frequencies above 10 exahertz (or >1019 Hz), and therefore have energies above 100 keV and wavelengths less than 10 picometers (10^−11 meter)
Gamma rays typically have frequencies above 10 exahertz (or >1019 Hz), and therefore have energies above 100 keV and wavelengths less than 10 picometers (10^−11 meter)
LinkWavelength and the Index of Refraction
Light travels as waves, with the wavefronts perpendicular to the direction of motion. In the animation shown here, the wavefronts are represented by the green parallel lines. The red arrow represents the direction of motion. As light moves from air into water, it not only slows, but the wavelength changes. The animation below illustrates how the wavelength becomes shorter in the denser medium of water. To replay an animation, click on "replay". Once you have viewed the first animation, click on "2" to continue.
Interestingly enough, the frequency of the waves does not change as the light moves from air to water. As we saw in the Review page, the wave's speed v is related to both the frequency f and the wavelength :
v = f.
Combining the above expression for velocity with the definition of index of refraction, we find a relationship between the wavelength = v/f in a medium and the wavelength 0 = c/f in vacuum:
In the above equation, the frequencies cancel because frequency does not change as light moves from one medium to another.
This is the operative part:
The ratio of wavelengths should be equal to refractive index.
In the above equation, the frequencies cancel because frequency does not change as light moves from one medium to another.
So, wavelength of light in vacuum/wavelength of gamma ray(light in sun) = refractive index of sun
Wavelength of light is in nanometers = 10^-9.
wavelength of gamma rays is supposed to be picometers = 10^-12.
So, refractive index of sun = (10^-9)/(10^-12) = 10^3 = 1000.
So, according to the mainstream numbers. Density of sun is around 1.4 g/cm^3. Refractive index must be around 1000.
If refractive index is 1000, then the speed of light in sun must be:
refractive index of sun = speed of light/ speed of gamma rays(light in sun)
1000 = 300,000,000/x
x = 3,000,000 m/s.
If this is the speed of gamma rays(light) in sun, then it should take how much time to cover a distance of 696,000 *10^3 m?
speed = distance/time.
time = distance/speed.
time = (696,000 *10^3)/(3,000,000) seconds.
time = 696/3 seconds.
time = 232 seconds.
time = 232/60 minutes.
time = 3.8 minutes or 4 minutes.
But, they say that it takes 4000 years.
Re: Physics Thread.
So, heat is not molecule vibration? And sun releases heat directly? And that sun's heat then travels through the vacuum of space?LokeshC wrote:Vacuum transmits heat.. Time to move to GDF phijjiks dhaaga???
Heat transfer occur through conduction, convection AND radiation(as in EM radiation)
Re: Physics Thread.
Saik and others .. if interested ... (I am going to ignore UB/JohneeG, they are free to think and post what they wish)
As I have posted multiple times recently ... (and a common knowledge to any physicist)..
c = Velocity of light in vacuum is constant and maximum possible velocity of any particle or transmission of information... (Means you can not send information faster than c)
But as said above (again by Bade) light slows down (it depends on its wavelength) if it passes through
air, or water, or glass..
Please read this for example" viewtopic.php?p=1832404#p1832404 or recent viewtopic.php?p=1979052#p1979052 (Please do read, there is a lot of information, quite carefully written)
Probably record is (by Lene V Hau of Harvard) is less than 40 miles/hour.. that's right slower than a car. (Check out https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EK6HxdUQm5s
(She used Bose condensate. (It is named for Indian Physicist Satyendra Nath Bose))
As I have posted multiple times recently ... (and a common knowledge to any physicist)..
c = Velocity of light in vacuum is constant and maximum possible velocity of any particle or transmission of information... (Means you can not send information faster than c)
But as said above (again by Bade) light slows down (it depends on its wavelength) if it passes through
air, or water, or glass..
Please read this for example" viewtopic.php?p=1832404#p1832404 or recent viewtopic.php?p=1979052#p1979052 (Please do read, there is a lot of information, quite carefully written)
Probably record is (by Lene V Hau of Harvard) is less than 40 miles/hour.. that's right slower than a car. (Check out https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EK6HxdUQm5s
(She used Bose condensate. (It is named for Indian Physicist Satyendra Nath Bose))
Re: Physics Thread.
But what is missing in above list is Bose-Einstein condensate.. where refractive index is about 5000!refractive index(which is based on density) = speed of light in vacuum/ speed of light in the medium.
So, here is a list of refractive indices:
vacuum(density -0) - refractive index -1.
air - 1.0001.
water - 1.333
ice(0.9 gm/cm3) - 1.3
glass - 1.5
diamond (4 gm/cm3) - 2.5
Notice that the refractive index does not even cross 5.
Cheers..

