Russian Weapons & Military Technology
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
You need 50 to make it go into drone mode. Read the article again. If you do not see it, that means you are not reading it properly.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
ATV Russian rover "Vityaz" for Troops & Cargo
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russian Aerospace Forces Equipment to Receive Full Lifecycle Maintenance in 2017
https://en.ria.ru/military/201612101048 ... ent/[quote]
Russia's Aerospace Forces Commander Col. Gen. Viktor Bondarev said that full lifecycle maintenance would be able to quickly supply components and blocks necessary for any type of flying vehicles, thus, enabling military personnel to repair the equipment faster.
MOSCOW (Sputnik) — All types of Russian Aerospace Forces' equipment will receive full lifecycle maintenance starting from January 1, 2017, Russia's Aerospace Forces Commander Col. Gen. Viktor Bondarev told journalists on Saturday.
Not only PAK FA (fifth generation fighters) will be receiving full lifecycle maintenance from January 2017, but all other Russian Aerospace Forces' equipment as well. It includes military, frontline, long-range and military transport equipment," Bondarev said at the celebrations dedicated to the centenary of the aviation engineering service.
Bondarev added that full lifecycle maintenance would be able to quickly supply components and blocks necessary for any type of flying vehicles, thus, enabling military personnel to repair the equipment faster, improving the correct functioning of the vehicles and increasing pilots' length of total flight hours.
"The modern technologies exclude a possibility of an aircraft taking off in a poor condition," Bondarev said. Engineer and aviation units celebrate the centenary of Russian aviation engineering service, which dates back to December 7, 1916, when the first department responsible for the maintenance of aircraft was opened.[/quote]
https://en.ria.ru/military/201612101048 ... ent/[quote]
Russia's Aerospace Forces Commander Col. Gen. Viktor Bondarev said that full lifecycle maintenance would be able to quickly supply components and blocks necessary for any type of flying vehicles, thus, enabling military personnel to repair the equipment faster.
MOSCOW (Sputnik) — All types of Russian Aerospace Forces' equipment will receive full lifecycle maintenance starting from January 1, 2017, Russia's Aerospace Forces Commander Col. Gen. Viktor Bondarev told journalists on Saturday.
Not only PAK FA (fifth generation fighters) will be receiving full lifecycle maintenance from January 2017, but all other Russian Aerospace Forces' equipment as well. It includes military, frontline, long-range and military transport equipment," Bondarev said at the celebrations dedicated to the centenary of the aviation engineering service.
Bondarev added that full lifecycle maintenance would be able to quickly supply components and blocks necessary for any type of flying vehicles, thus, enabling military personnel to repair the equipment faster, improving the correct functioning of the vehicles and increasing pilots' length of total flight hours.
"The modern technologies exclude a possibility of an aircraft taking off in a poor condition," Bondarev said. Engineer and aviation units celebrate the centenary of Russian aviation engineering service, which dates back to December 7, 1916, when the first department responsible for the maintenance of aircraft was opened.[/quote]
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Classified. Work fighters Russian special operations forces in Syria. Unique footage
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russia announces new drone sub that can mimic any other submersible vessel
A Russian-owned media outlet announced plans for the new submersible drone this week. The drone, called Surrogat, has been designed to “realistically reproduce the physical fields of the enemy—the acoustic and electromagnetic.” In other words, it’s been designed to mimic the signals produced by submarines, potentially fooling enemy vessels into thinking it’s any number of different submersible ships.
The Rubin Design Bureau, famed for their development of cold war era Russian submarines such as the gigantic Typhoon Class missile sub, announced that they have been developing the new submersible drone in cooperation with the Russian Navy. The Surrogat will be fifty-five feet long and capable of diving for fifteen to sixteen hours at a time. It is planned to weigh approximately fifty tons and will be capable of reaching depths of six hundred meters using a lithium-ion battery power source. Plans call for the submersible to travel at speeds “in excess of 24 knots” with a maximum range of six hundred miles.
https://sofrep.com/69510/russia-announc ... le-vessel/
A Russian-owned media outlet announced plans for the new submersible drone this week. The drone, called Surrogat, has been designed to “realistically reproduce the physical fields of the enemy—the acoustic and electromagnetic.” In other words, it’s been designed to mimic the signals produced by submarines, potentially fooling enemy vessels into thinking it’s any number of different submersible ships.
The Rubin Design Bureau, famed for their development of cold war era Russian submarines such as the gigantic Typhoon Class missile sub, announced that they have been developing the new submersible drone in cooperation with the Russian Navy. The Surrogat will be fifty-five feet long and capable of diving for fifteen to sixteen hours at a time. It is planned to weigh approximately fifty tons and will be capable of reaching depths of six hundred meters using a lithium-ion battery power source. Plans call for the submersible to travel at speeds “in excess of 24 knots” with a maximum range of six hundred miles.
https://sofrep.com/69510/russia-announc ... le-vessel/
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Truly frightening.I'll try and get more details from Polmar's work later.
http://ameriforce.net/russias-tests-new ... -us-coast/
http://ameriforce.net/russias-tests-new ... -us-coast/
Russia tests its new autonomous nuclear submarine off the US coast
17 hours agoby William Worth861 Views5 min read
After an apparent leak by a Russian news outlet it has emerged that Russia has been testing a “terrifying new autonomous drone submarine” capable of carrying nuclear warheads in waters off of the US East coast.
The top secret nuclear capable sub, code named “Kanyon” by the Pentagon, allegedly has a displacement of 40 tonnes, a range of up to 6,200 miles and a top speed of 56 knots. US security officials say that they first detected the test of the new system on November 27 after it was launched from a Sarov class submarine – although they didn’t reveal the location.
The drone submarine is further evidence of what US officials say is an “aggressive Russian strategic nuclear forces modernization program” and officials familiar with details of the Kanyon program said the weapon is envisioned as an autonomous submarine first strike vehicle that can be armed with nuclear warheads that range in size to “tens” of megatons – one megaton alone having a destructive power dozens of times that of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bombs.
When sat atop missiles megaton warheads are often called “city busters” because they are designed to destroy entire metropolitan areas or blast buried targets and an underwater megaton-class drone weapon could be used to knock out harbours and coastal regions, said officials who declined to be named due to the sensitivity of the information.
“This is an unmanned sub that will have a high-speed and long-distance capability,” said one official, who noted that the drone development is years away from being deployed.
The existence of Kanyon will no doubt further complicate the US’ own nuclear strategy.
“It’s very difficult to consider Russia a responsible party when it’s developing something like this,” the official said.
Another official familiar with the program said that the Kanyon will be a large nuclear-powered autonomous submarine. This official said the size of its nuclear warhead is not clear.
Russian leaders announced their new maritime strategy in July and provided hints about the new drone sub, based on a doctrine that calls for the development of new innovative technologies – including unmanned underwater vehicles.
Lt. Col. Michelle Baldanza, a Pentagon spokeswoman, declined to comment on the nuclear-armed underwater drone.
The Pentagon said last week that it is closely watching a Russian military research ship that sailed along the east coast of the US, the ship, a research vessel called the Yantar, was engaged in underwater reconnaissance, gathering intelligence that could be used to support a weapon system like the nuclear UUV.
While the US currently has no similar plans for a megaton-class underwater nuclear strike vehicle the US Navy is developing a range of UUVs – including a weapons carrying drone.
“The Kanyon represents another example of Russia’s aggressive and innovative approach to the development of military capabilities against US and Western interests,” said Jack Caravelli, a former CIA analyst who specialized in Soviet and Russian affairs.
“The possible yield of the warhead, in the megaton class, clearly is an attempt to inflict catastrophic damage against US or European naval facilities or coastal cities,” he added, “nations vote with their resources, and the Kanyon, along with an expanding number of other military modernization programs, indicates the priority Vladimir Putin places on military preparedness against the West.”
Meanwhile Mark Schneider, a former Pentagon nuclear policymaker, said Russian state-run media, such as RIA Novosti, as well as a string of Russian weapons engineers have continuously announced plans for more UUV development.
“In 2014, Putin stated that there were undisclosed strategic nuclear modernization programs that would be made public at the appropriate time,” said Schneider, “and this might be one of those announcements.”
“Our institute already concluded a number of new developments in the sphere of command systems automation [including] remotely operated, unmanned sea based underwater vehicles. We hope that these developments will be applied for designing of a new destroyer vessel,” said Lev Klyachko, director of the Russian Central Research Institute.
Robert Kehler, who retired two years ago as commander of the US Strategic Command, said development of a robot underwater nuclear strike vehicle could be part of what he termed a “troubling” Russian strategic nuclear buildup.
“Overall, we were watching the Russian nuclear modernization effort very carefully,” said Kehler.
Norman Polmar, a naval analyst and author, said the Kanyon could be based on a Soviet era nuclear torpedo disclosed in his 2003 book, “Cold War Submarines.”
Both the Russian Navy and its Soviet predecessor, have been innovators of undersea systems and weapons.
“These efforts have resulted in some of the world’s most advanced torpedoes,” said Polmar, “early in the nuclear age, the Soviets began development of a massive torpedo for attacking coastal cities and ports.”
The T-15 torpedo was about 75 feet long and was capable of carrying a high-yield thermonuclear warhead some 15 miles underwater, something Polmar called “a truly innovative concept.”
“While unmanned technology itself is not new, the potential impact these systems will have on the way we operate is almost incalculable,” said Ray Maybus, US Navy Secretary in a speech in April.
Russia aren’t alone in their pursuit of the development of new drone UUV’s though, there are a flotilla of countries prioritising the tech, including the US, but at the moment it looks like Russia are the only ones who are developing a first strike UUV weapon. If history teaches us anything though it’s that where one country leads others will follow…
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
That news was propagated by free becon site which is CT website and copied by other news outlets , nothing credible about it
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Well,there are other reports posted earlier of the same.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russia upgrading older tanks with Armata fire control and getting first 100 new Armata tanks
http://www.nextbigfuture.com/2016/12/ru ... -with.html
http://www.nextbigfuture.com/2016/12/ru ... -with.html
The Russian Defense Ministry has a contract with Uralvagonzavod (UVZ), the world’s largest tank maker, for the first batch of 100 third-generation T-14 main battle tank (MBT), an armored vehicle based on the “Armata” universal chassis system, according to local media reports. Russia plans to acquire 2300 T-14 Armata's by 2025. Previously Rusgetsia was going to get the 2300 Armata's by 2020.The T-14 was originally priced at about $8 million. According to some Russian defense officials, the price will come down to around 250 million rubles ($3.8 million) per unit once serial production begins.Russia may upgrade parts of its T-72 and T-90 main battle tank (MBT) fleets with the automatic target tracker (ATT) and fire control computer (FCC) installed in the Armata T-14 MBT, which is now entering production at UralVagonZavod's Nizhny Tagil facility.The installation of the ATT and the FCC from the T-14 Armata will improve the first round hit capability of the older T-72 and T-90 MBTs under adverse battlefield conditions, as well as reducing the workload on the gunner.Once locked on, the ATT constantly tracks the target and lays on the 125 mm smoothbore gun as well as taking into account inputs from the sensors, such as the speed and direction of the platform, condition of the gun, and ambient weather. The gunner then decides when to engage the target.The T-72B3 and T-90 MBTs selected to be upgraded will be those already fitted with the Kalina computerised fire control system (FCS), the latest version of which is installed in the T-14 Armata.
The T-72B3 has been deployed on operations on the Russia/Ukraine border where it has demonstrated a high level of survivability because it is fitted with the latest generation Kontakt-5 explosive reactive armour (ERA), which provides protection not only against missiles and rockets fitted with a high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead, but also kinetic energy projectiles.The decision to further enhance the capabilities of at least part of its existing MBT fleet could indicate that Russia will not replace the T-72 and subsequently the T-90 MBTs with the T-14 Armata on a one-for-one basis in the near term, and will continue to deploy a mixed MBT fleet.Russia has already decided to upgrade part of its T-80BV turbine-powered MBTs to extend their operational life, with the first of these to be handed over in 2017 from UralVagonZavod's Omsk facility.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
There was another report,not posted, which said that Russia was rehabilitating large number of its older T-72 and T-80 MBTs.The western conclusion was that perhaps the Ru def min was cash strapped for new tanks and was keeping numbers happy upgrading the old ones. Well,we're doing the very same thing with our t-72s,being upgraded at comparatively low cost. The above post indicates that with the new ERA panels,the survivability of legacy T-72s and T-80s has been significantly enhanced. Armies all over the world are doing the same thing. Second point was that perhaps the Armata T-14 hadn't been fully developed accounting for the slow production rate.
Plausible,however,budgetary considerations seem more likely. In modernisation of the Ru def foces,N-subs clearly is the highest priority. There is a report out today that the very first N-sub of Russia is being rehabilitated to be sent back to sea. Various Sov. era N-subs have been modernised for both research and mil duties.The phenomenal strength of Ru subs' hulls is well known with evidence from both the Kursk and SRakshak tragedies. Both subs were completely salvaged with their hills mote or less intact apart from the torpedo compartment.Similarly old T-72 MBTs with new ERA armoour panels,engines and sensors would bring them almost upto t-90 stds. The T-80s with their GT engines would be more useful in certain theatres than T-72s.These tanks could be in service for another 15 yrs at least. See how legacy T-55s are still battling it out in ME wars. Ru modernisation of legact MBTs seems to be based upon pragmatism and cost saving ,instead of expensive one-for-one replacements with new MBTs.
Plausible,however,budgetary considerations seem more likely. In modernisation of the Ru def foces,N-subs clearly is the highest priority. There is a report out today that the very first N-sub of Russia is being rehabilitated to be sent back to sea. Various Sov. era N-subs have been modernised for both research and mil duties.The phenomenal strength of Ru subs' hulls is well known with evidence from both the Kursk and SRakshak tragedies. Both subs were completely salvaged with their hills mote or less intact apart from the torpedo compartment.Similarly old T-72 MBTs with new ERA armoour panels,engines and sensors would bring them almost upto t-90 stds. The T-80s with their GT engines would be more useful in certain theatres than T-72s.These tanks could be in service for another 15 yrs at least. See how legacy T-55s are still battling it out in ME wars. Ru modernisation of legact MBTs seems to be based upon pragmatism and cost saving ,instead of expensive one-for-one replacements with new MBTs.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
MiG-35. Not sure if its just a souped up MiG-29K. not sure if it has an AESA radar either.
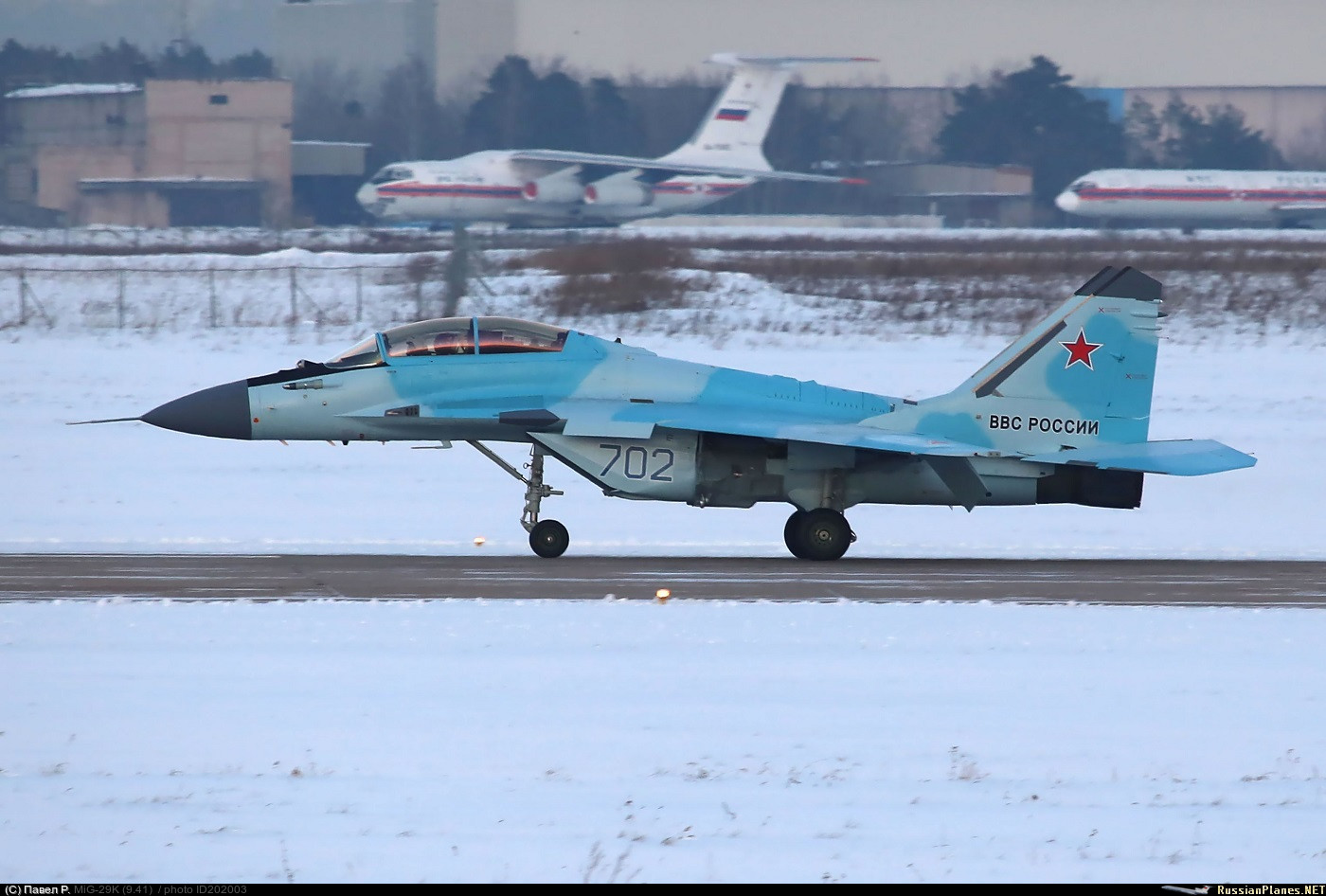


Re: Russian weapons and military technology
The sky over Moscow will cover the new radar that can detect stealth missile

MOSCOW, December 15. / TASS /. The new mobile radar station (RLS) combat mode "approaching", the ability to detect stealth cruise-missiles at extremely low altitudes, to intercede on combat duty in the Moscow Radio Engineering Regiment Aerospace Forces. This was reported in the press service of the Russian Defense Ministry
"The station is able to automatically detect, coordinate, implement the capture and maintenance of various air targets, including planes, helicopters, cruise missiles, including those made by the technology." Stealth "capabilities station can simultaneously be accompanied by no less than 200 goals at an altitude of more than 10 km and at a distance of over 200 km, "- said in a statement.
In addition, the "approaching" radar can determine the nationality of the goals. As clarified in the press service, the station is designed to detect and track airborne targets at low and extremely low altitudes. At the same time it is protected from active and passive noise and combined with digital array antenna. Radar consists of three transport units and may be rolled for 10 minutes.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Radio engineering troops celebrate its 65th anniversary
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
December 17 - Day of the Strategic Missile Forces
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russian Navy receives first upgraded Ka-27M

The first upgraded Ka-27M 'Helix' anti-submarine warfare was delivered to the Russian Navy by KumAPP in mid-December. Source: Russian Helicopters

The first upgraded Ka-27M 'Helix' anti-submarine warfare was delivered to the Russian Navy by KumAPP in mid-December. Source: Russian Helicopters
The Kumertau Aircraft Production Enterprise (KumAPP) has handed over the first modernised Ka-72M anti-submarine warfare (ASW) helicopter to the Russian Navy, Russian Helicopters announced on 19 December.
A first batch of eight Ka-27Ms is set to be delivered to the Russian Ministry of Defence by the end of the year, Vladislav Savelyev, deputy chief executive officer for sales of Russian Helicopters, stated.
The helicopters will be deployed to air bases attached to Russia's Black Sea and Northern Fleets, and also to the Yeysk naval aviation training centre.
The Kumertau factory began repairs (in order to extend service life) and upgrades of these eight helicopters to Ka-27M standard at the beginning of 2015. Russia's National Armament Programme provides for the upgrade of 46 helicopters to Ka-27M standard by 2018, the number planned to be kept after 2020. However, only two upgrade contracts have been signed as of yet, for a total of 22 helicopters (eight plus 14).
The Ka-27M (also designated izdeliye 27D2) upgrade programme was launched in the early 2000s. The helicopter's rotor system, powerplant, and airframe are unchanged while the mission system is completely new. The Ka-27M's mission system includes the Phazotron-NIIR Bumerang (Boomerang) radar command-tactical system, integrated around the helicopter's FHA radar; the new Kema radio sonobuoy system with RGB-16MK buoys; upgraded Ros'-VM dipping sonar; new MMS-27 fixed magnetic anomaly detector; electronic support measures suite; data link; a navigator's tactical display; and a SSP-V-27M satellite system for deck landings.
The Ka-27M can be armed with all available Russian weapons in the appropriate class, including APR-3 anti-submarine rocket torpedoes.
The FHA radar alone, without the other elements of the mission system, has been proposed as an upgrade for Russia's Ka-27PS search and rescue helicopters.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Borei SSBN

Yasen SSGN

Yasen SSGN
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
The atom briefcase Yeltsin. On show at the Boris Yeltsin Presidential Center, Yekaterinburg
https://twitter.com/StevenDerix/status/ ... 2469151744
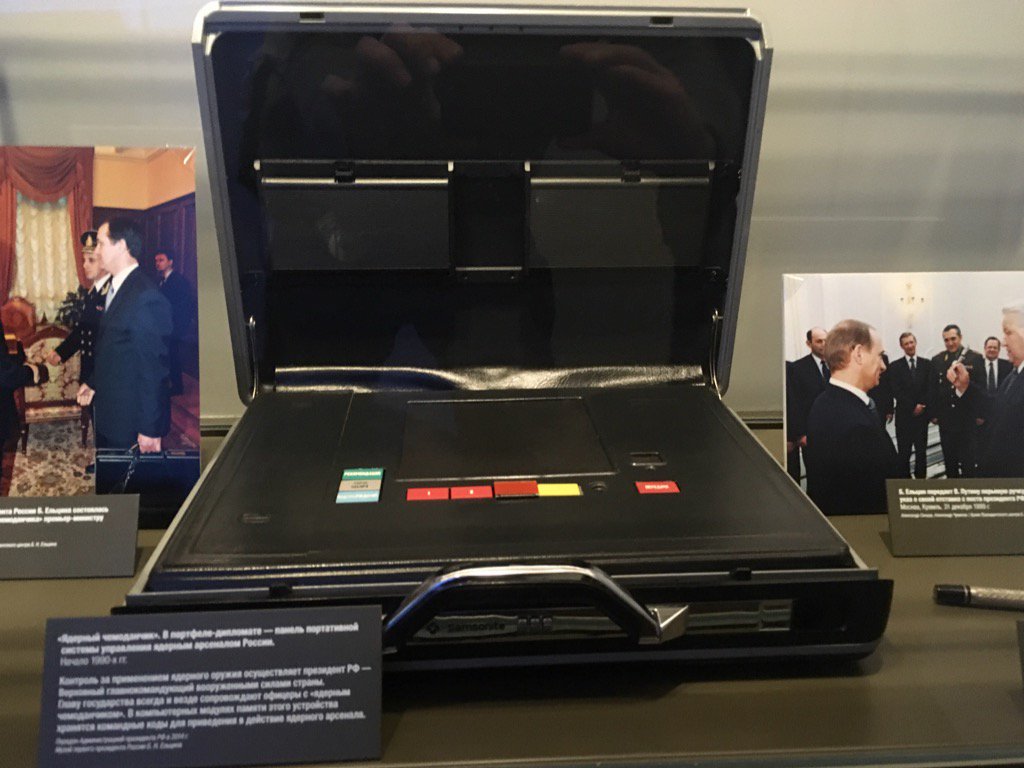

https://twitter.com/StevenDerix/status/ ... 2469151744

Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russia tested over 160 new weapons in Syrian operation – defense minister
https://www.rt.com/news/371302-russian- ... al-report/
https://www.rt.com/news/371302-russian- ... al-report/
While the primary goal of Russia’s military operation in Syria is to prevent the disintegration of the country, it has also provided a chance to field-test 162 advanced Russian weapons, Russia’s defense minister reported.
“During the operation in Syria, 162 advanced and upgraded weapons have been tested in combat. They have proven to be highly efficient,” Sergey Shoigu told a Thursday meeting of senior Russian officials. The session, chaired by President Vladimir Putin, was focused on the annual report of the minister.
Among the systems tested in Syria were Su-30SM and Su-34 fighter jets, Mi-28N and Ka-52 helicopters, and Kalibr cruise missiles, as well as other arms. According to Shoigu, 10 of the 162 weapons tested revealed flaws that had not been identified on test ranges, prompting the ministry to stop buying them and ask the developers to fix them.
Shoigu said Russia’s involvement has “prevented the disintegration of the Syrian state, broken the chain of ‘color revolutions’ in the Middle East and North Africa, and launched a process for reaching a political settlement and reconciliation between warring parties.”
So far, 18,800 sorties and 71,000 airstrikes have been carried out by the Russian Air Force as part of the operation, the minister said. Russian warplanes have hit hundreds of militant training camps, arms workshops, military vehicles, and artillery systems.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Just throwing a "stealth looking" aircraft chasis around a 4th generation aircraft does not make it 5th generation.
This raises the question about claims of PAK-FA, J-20, J-31..etc all of which claim to be 5th generation but may well be nothing more than 4th generation (or in some cases 3+ generation) aircraft with a fancy "stealth looking" chasis thrown around it.
In essence old wine in a new bottle but sold at an escalated price with an escalated development cost - the bill of which is simply sent to India to pay.
Be careful of equating external looks to 5th generation without examining what actually is in the aircraft.
I don't know what we are getting in terms of national aerospace industrial development for paying all these billions in R&D money to overseas plane manufactruers - probably a nice receipt.
This raises the question about claims of PAK-FA, J-20, J-31..etc all of which claim to be 5th generation but may well be nothing more than 4th generation (or in some cases 3+ generation) aircraft with a fancy "stealth looking" chasis thrown around it.
In essence old wine in a new bottle but sold at an escalated price with an escalated development cost - the bill of which is simply sent to India to pay.
Be careful of equating external looks to 5th generation without examining what actually is in the aircraft.
I don't know what we are getting in terms of national aerospace industrial development for paying all these billions in R&D money to overseas plane manufactruers - probably a nice receipt.
Air Chief Marshal Raha when asked about status of Fifth-generation fighter aircraft (FGFA) while addressing his last Press conference before his retirement , confirmed that negotiations for development of 5th Generation fighter aircraft based on Russian T-50 is still be carried out but refused to confirm that final agreement between India and Russia will be concluded anytime soon.
High-level Russian delegation earlier this year had talks with Indian officials In India, where they offered to reduce developmental cost from $6 billion to $3.7 billion to fund and develop customised FGFA based on Indian Air force requirements which also included development of three prototypes of FGFA fighters to be delivered to India for testing and product optimization.
Sergei Chemezov, CEO of Rostec State Corporation while speaking to the Indian media had said that they are hopeful that final agreement on development of FGFA will be concluded by year end but IAF is not yet fully on board the project and in past has questioned Russians on key technologies developed for T-50 which IAF claims is not fully matured enough to categorise T-50 has a True 5th generation fighter jet in lines with American developed F-35 and F22 5th generation fighter jets .
Highly reliable sources close to idrw.org have predicted that Indian and Russian officials will have another round of negotiation at sidelines of Aero India 2017 to be held in February next year in Bangalore and there are high hopes that Russian officials will come up with better technical proposal to break the deadlock like they did in 2016 by reducing developmental cost of FGFA.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Unmanned aerial vehicles "Outpost" (IAI Searcher Mk II) assembled in Russia
http://bmpd.livejournal.com/2354007.html
http://bmpd.livejournal.com/2354007.html
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russian Government has Approved development of PD-35 engine of 35T Thrust to be completed by 2025 , this one to be used for Wide Body Aircraft and Transport Aircraft

http://www.ato.ru/content/oak-i-odk-pod ... =frs&pos=8The Russian government intends to support the aerospace industry due to excessive dividends "Rosneftegas" and proceeds from the sale of shares of "Rosneft" owned "Rosneftegas". As stated in the relevant orders Dmitry Medvedev's prime minister, published this week, the proceeds will be sent to the United Engine Corporation (UEC) and the United avaiastroitelnuyu Corporation (UAC) for certain projects.
JDC will receive 783 million rubles. the development and organization of serial production TV7-117 engine turboprop for regional aircraft IL-114, and 1.5 billion rubles. - To develop a promising power plant ultra traction PD-35, designed for long-haul civil aircraft.
KLA could count on 1.517 billion rubles. for the development and serial production of the IL-114 and 2.4 billion rubles. for the modernization of wide-body aircraft IL-96. The corresponding contributions to the authorized capital of the Corporation will be required to make the Ministry of Industry.
According to the documents, additional capitalization can be smaller, ie. To. Be carried out "in the case and within the revenue of the federal budget revenues from dividends of JSC" Rosneftegas "(owned by the Russian Federation), in excess of the amount of 36.039 billion rubles., And sverhpostupleny related with the implementation of the package of shares of PJSC "Rosneft" owned "Rosneftegas".
The fact that the government intends to allocate additional funds to support the Il-114 and Il-96-400 projects, in May of this year, said Deputy Prime Minister Dmitry Rogozin. Deputy Minister of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation Andrey Boginsky in August said that the financing of the project of the Russian Regional Jet will begin at the end of 2016. This year was supposed to invest more than 2.6 billion rubles. Recall, the final assembly of the IL-114 will be made at the aircraft plant "Sokol". The first flight is scheduled for 2019 and the first supplies - in 2021 on the whole, the IL-114 and IL-96 modernization projects planned to allocate about 50 billion rubles.
Recall that the engine PD-35 , including to be installed on the modernized Il-96. The development of the power plant began in the UEC this year.

Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Il-112 progress:






















Re: Russian weapons and military technology
https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/che ... h-in-2017/
Russia readies two of its most advanced submarines for launch in 2017
By Thomas Gibbons-Neff December 29, 2016
This July 2, 2009, photo shows a Russian nuclear submarine, Yuri Dolgoruky, near the Sevmash factory in the northern city of Arkhangelsk, Russia. (Alexander Zemlianichenko, Associated Press)
Two of Russia’s most advanced nuclear submarines will be launched in 2017, despite ballooning program costs and delays, according to a report by a Russian state news agency.
Vice Adm. Viktor Bursuk, deputy commander of the Russian navy, said last week that the ballistic-missile-carrying, Borei-class Prince Vladimir and the Yasen-M attack boat Kazan “will be floated out” by the end of next year. While there had been reports that the vessels would be delayed, Bursuk said the navy expects to take possession of the vessels “within the time limits stipulated by the contract.”
The terms “launched” and “floated out” do not necessarily mean the vessels will be ready for sea trials and commissioning. Once they move from the shipyard to their docks, more systems will likely need to be installed.
[Report: Russian sub activity returns to Cold War levels]
The Borei- and Yasen-class boats endured a tortuous development cycle as money dried up after the collapse of the Soviet Union. Even though the keel of the Yury Dolgoruky, the lead boat of the Borei class, was laid down in 1996, the nearly two-football-field-long sub wouldn’t join the Russian fleet until 2013. Likewise, the initial Yasen-class vessel, the Severodvinsk, first underwent construction in 1993 only to earn its commission 20 years later.
Though two other Borei-class submarines have entered service following the commissioning of the Dolgoruky, the Prince Vladimir will be the first of four more advanced Borei-type subs, known as the Borei-A class, that will enter the Russian fleet. Construction began on the Vladimir in 2012, and in the coming years, eight Borei-class submarines — five A-types and the three current variants — will be at sea. On Friday, the keel of the eighth and likely final Borei-A class, the Prince Pozharsky, was laid down.
A 2013 article written by a U.S. naval officer for Proceedings magazine discussed the importance of the Borei- and Yasen-class submarines. Lt. Cmdr. Tom Spahn argued that the Borei and Yasen classes would become the backbone of the Russian sub fleet as the Russian navy sought to consolidate the capabilities of its different classes of submarines into two types.
The Borei — which means North Wind — costs roughly $890 million, according to Spahn and has a silent propulsion technology much like the new U.S. Virginia attack-class nuclear submarines. The Borei is also capable of carrying 16 ballistic missiles, while the Borei-A class is rumored to carry 20.
The Yasen class, or Ash Tree, is designed primarily to attack other subs, surface ships and gather intelligence and requires a crew of only around 90, compared with the Virginia class’s 134. Spahn said that the relatively small crew size indicates an advanced level of autonomy in the Russian sub.
[As Russia scopes undersea cables, a shadow of the United States’ Cold War past]
The small crew size and high-tech systems might have something to do with its price tag, as the initial Yasen boat, the Severodvinsk, costs roughly $1.5 billion. The second vessel, the Kazan will likely cost double that by the time it takes to the sea. The Yasen, according to Spahn’s piece, has eight torpedo tubes, capable of launching underwater projectiles that can reach roughly 230 mph. The Yasen class can also carry a wide array of cruise missiles. In April, the Severodvinsk successfully test fired Kalibr cruise missiles, the same type of weapons Russia fired into Syria.
Russian submarine activity has steadily increased since Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea in Ukraine. In February, a top NATO admiral, Royal Navy Vice Adm. Clive Johnstone, said that NATO sub commanders are reporting “more activity from Russian submarines than we’ve seen since the days of the Cold War.” Earlier this month, news reports indicated that two Oscar-II class Russian cruise missile submarines were operating near a U.S. and French aircraft carrier sailing in the eastern Mediterranean, setting off a NATO-led hunt for the boats.
The Russian navy has dozens of submarines, the majority of which are Soviet-era nuclear and diesel-powered subs. While Russia is trying to churn out new vessels, its navy is also modernizing some of its older boats. The U.S. Navy, however, has upward of 50 submarines, all of which run on nuclear propulsion. Congress’s most recent defense spending bill authorizes the construction of six Virginia-class submarines through 2019 and has allocated money to replace the aging Ohio-class ballistic missile submarine.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
"Russia"-special flight squadron (RSD) got 5 new a/c: Il-96-300, Il-96-300-PU(M1) command post, Tu-214SR com a/c + 2 SSJ-100 in 2016
https://twitter.com/RSS_40/status/815866345212563460
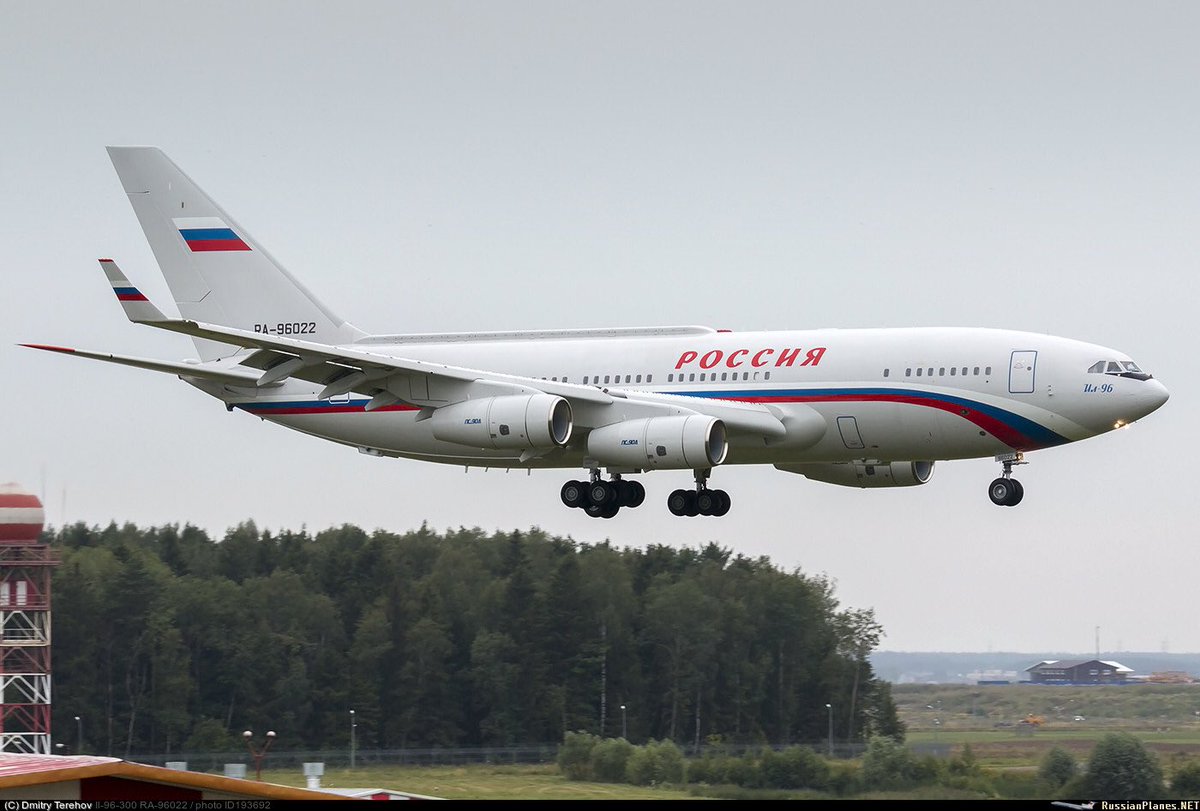
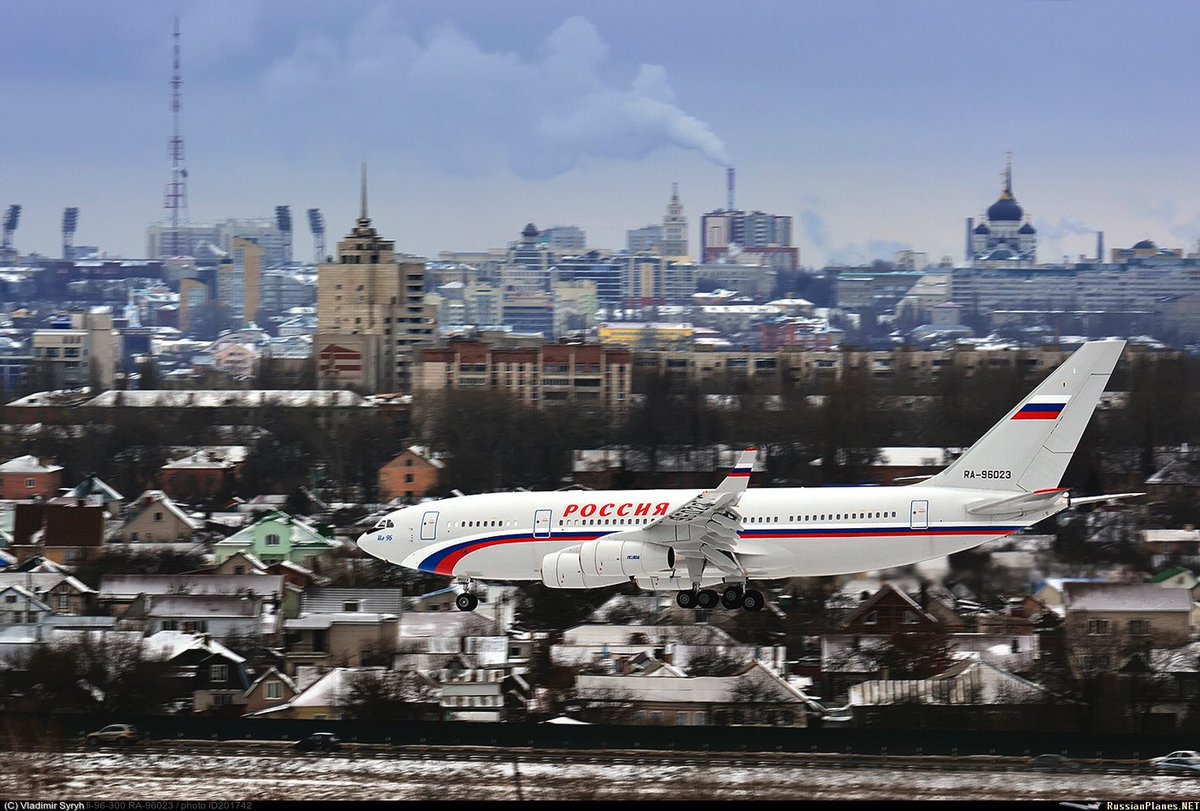
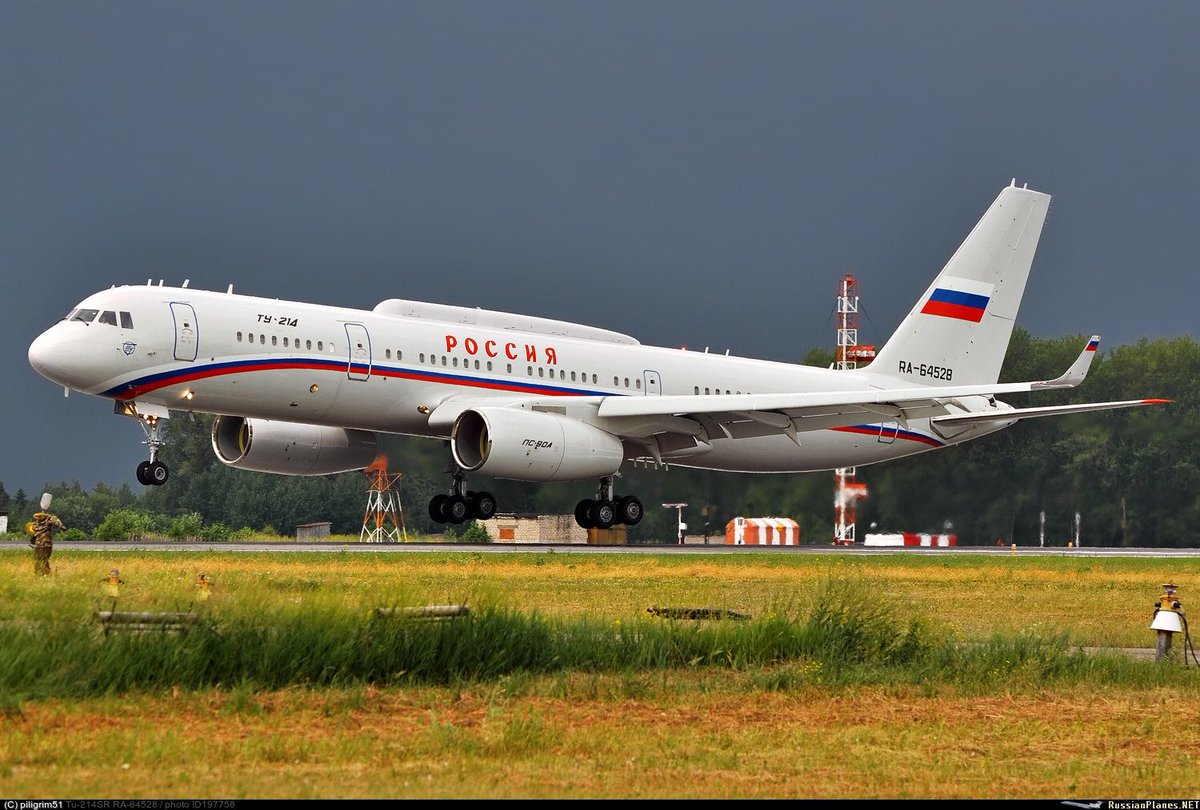
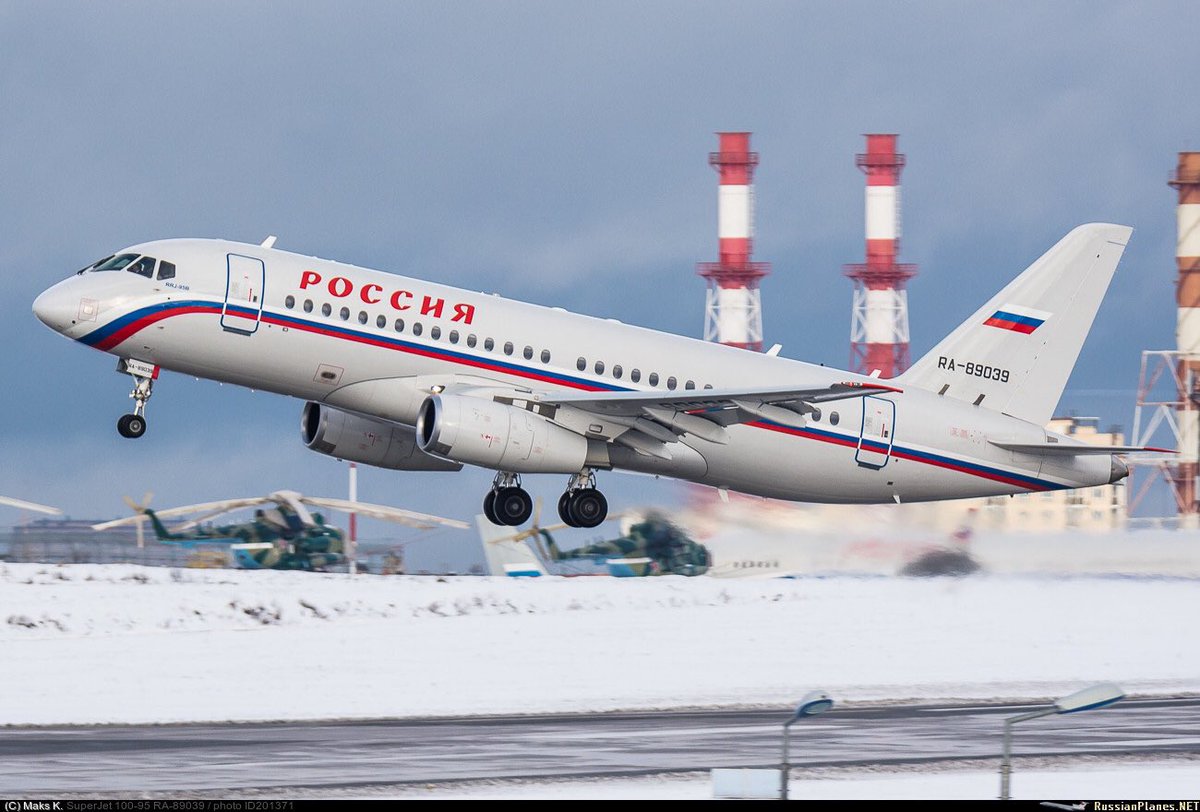
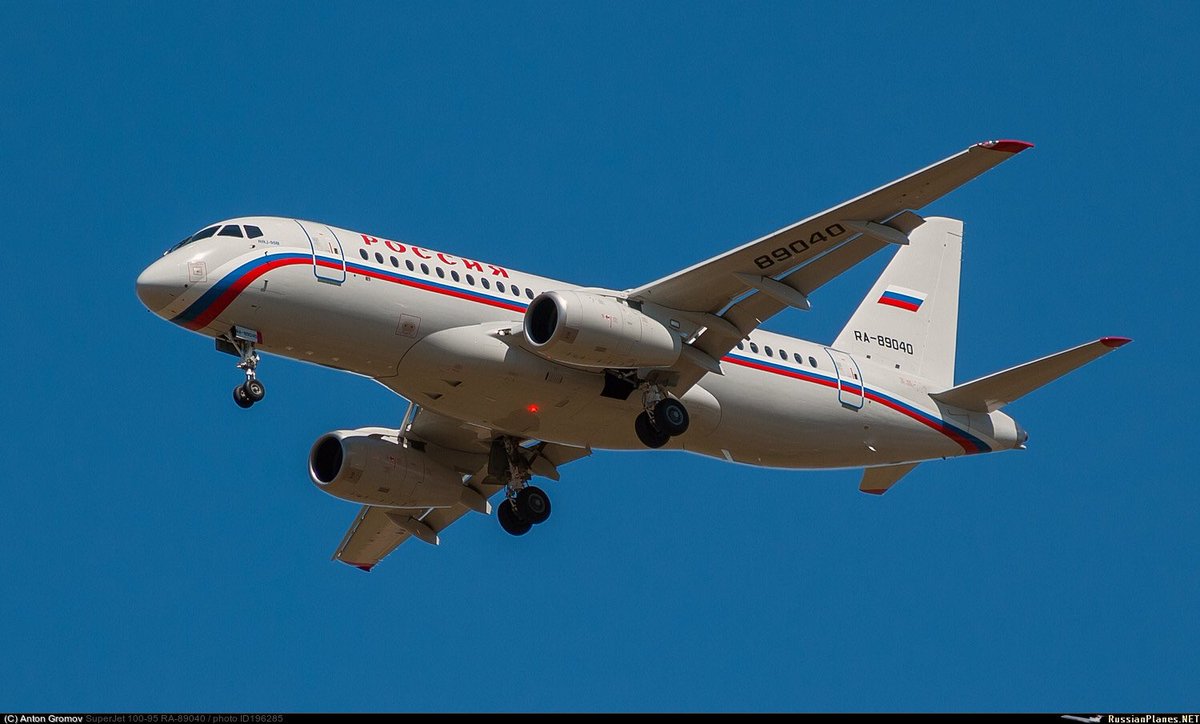





https://twitter.com/RSS_40/status/815866345212563460





Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Eyes for nuclear war
http://vpk.name/news/172059_glaza_dlya_ ... oinyi.html
Russia will restore the warning system missile attack on all fronts
http://vpk.name/news/172059_glaza_dlya_ ... oinyi.html
Russia will restore the warning system missile attack on all fronts
In 2017 in Russia will be the first time created a continuous radar field warning system missile attack. Fill the gaps with the collapse of the USSR in the early warning system will provide new radar station "Voronezh", able to see the launches of enemy missiles at a distance of up to 6 thousand. Km.
In December 2016, Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu at the extended board meeting of the Ministry of Defense reported to the President on the successful completion of state testing of three new radar stations (RLS), a high prefabrication: Orsk ( "Voronezh-M"), Barnaul ( "Voronezh-DM") , Yeniseysk ( "Voronezh-DM"). According to Shoigu, in 2017 they intercede on combat duty.
The commissioning of these three components of the missile attack warning will allow for the first time in Russia's recent history of the system set up around the perimeter of its borders continuous radar field in all strategic directions and in every possible flight trajectories of ballistic missiles, the minister stressed.
In addition, according to the head of the military department, conducted revision of three existing radar station in Baranovichi, Olenegorsk and Pechora. And in the near future the Ministry of Defense intends to completely replace the radar type "Voronezh" all Soviet early warning radar ballistic missile launches. These measures should dramatically increase the possibility of the national warning system of missile attack early warning system and the concentration of ground-based components entirely in the territory of Russia.
A single domestic EWS ceased to exist with the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991.
A significant part of the system of nodes (the radar type "Dnepr" and "DTV") remained on the territory of the newly independent states: in Skrunda (Latvia), Mukachevo, Sevastopol (Ukraine), Kutkashene (Azerbaijan), in the city of Balkhash and Cape Gulshad (Kazakhstan) .
With some of the new states subsequently failed to agree on the use of radar. However, most of the radars were either decommissioned or even blown up, as it did in 1995 with "Daryalom" Skrunda in Latvia.
Meanwhile, the warning system missile attack had significant gaps even in the years of the Soviet Union. There was not covered by the north-eastern sector. To close it, in 1970-1980-ies the construction of the respective radar began in the city of Yeniseisk (Krasnoyarsk region).
However, on the request of the United States, indicates a violation of the ABM Treaty in 1972, Mikhail Gorbachev ordered to completely destroy the radar under construction.
Thus, Russia inherited from the Soviet Union warning system with gaping holes and do not provide full national security. In the 1990s, the money to improve the early warning system is practically not allocated. Only in the second half of the 2000s, it began the construction of new radar.
The new units EWS steel radar meter 77YA6 range "Voronezh-M", developed and produced by JSC "Radio Engineering Institute named after Academician Mints," and the station decimeter 77YA6-DM range "Voronezh-DM", developed by JSC "Scientific-Industrial Complex" Research Institute of distant radio communication "(NFC NIIDAR).
They are fixed-horizon radar high prefabrication (VZG). The last characteristic is the modular principle and pre-fabricated structures on the site of the assembly, by which the construction of missile attack warning stations was reduced from years to 18 months.
"Voronezh" radar consists of a transceiver unit with active phased array (AESA), prefabricated buildings for personnel and several containers with electronic equipment.
Previously, only for cooling electronic equipment unique in its characteristics radar "Daryal" required three types of water, and its supply is ensured by more than three hundred motors from 5 to 10 kW. In addition, also required to build the water cooling means - different types of cooling towers.
Computing complex radar "Daryal" occupies an entire floor of a huge building.
Half of the electronic equipment has an analog type. The operation of "Daryal" provided 1,500 troops and officers.
The last of the "Daryalov" was put into operation in the first half of the 1980s. To the credit of the developers of this station, in many of their characteristics "Daryal" and today remains unsurpassed radar.
Now the installation of new radar early warning system is much less effort. All equipment "Voronezh" in container execution is delivered from the factory to build on pre-concreted area. Modern computing systems are no longer occupy an entire floor and about two closets. Power consumption "Voronezh" is only 0.7 MW. This is 50 times less than that consumed type radar "Daryal" in Azerbaijani Gabala (Kutkashene), for which the power supply worked a significant part of the neighboring Mingechevir hydroelectric power station capacity.
Target detection range "Voronezh-M", which operates in the meter range, up to 6 thousand. Km. "Voronezh-DM", which operates in the UHF range - up to 6 thousand kilometers over the horizon and up to 8 thousand km vertically...
Each radar can simultaneously detect and track up to 500 objects.
Radar "Voronezh-DM" deployed or are under construction at the stage of trial operation in Armavir, Krasnodar Territory, the village Pioneer Kaliningrad region, Yeniseisk (Ust-Kem village), Barnaul (grooms village) Altai Territory and the city of Zeya Amur region. "Voronezh-M" - in the village Lekhtusi Leningrad region, Orsk, Orenburg region, Usolye-Siberian (Mishelevka) Irkutsk Oblast and Vorkuta (town Vorgashor Komi Republic).
It is in Barnaul, Yeniseysk Orsk and works are most intense. According to interlocutors "Gazety.Ru" in the industry, "Voronezh-M" in Orsk will work in the sector of the Taklamakan desert to the shores of the Mediterranean. Locator, if necessary, ensure detection of missile launches from the Middle East, southern Europe, the Arabian Peninsula and North Africa. With the statement on combat duty this radar station become unnecessary at Cape Gulshad in Kazakhstan.
We also consider the question of the construction of the radar station "Voronezh" at Cape Chersonese in Sevastopol. Now it operates Soviet radar station "Dnepr". Over the years, being in a part of the Ukrainian Armed Forces station completely dilapidated, and it came into complete disrepair.
Completion of the deployment and commissioning of the entire series radar "Voronezh" will completely close the existing gaps in the northwest, southwest, south and southeast missile-dangerous directions. Russian early warning system will vserakursny, which failed to achieve even the Soviet Union.
In the future, the individual radars will be created so-called made by the receiving position (WFP) with reduced antenna, "tied" to the primary radar, which will significantly increase the chances of stable functioning early warning system in the conditions of intense opposition from the potential enemy.
With the deployment of more and more new units EWS it is possible to simultaneously support a ballistic target by several "Voronezh".
This will significantly build more precisely the trajectory of ballistic targets.
On the other hand, new challenges for the warning system puts the appearance of a potential enemy armed hypersonic maneuvering warheads and missiles of the next generation. Targets of this type require a continuous maintenance rather than two or three notches with a further trajectory calculation, as with conventional ballistic purposes.
The next step will be the development of early warning system of high-grade radar "Voronezh-VP", which is a further development of the station meter range. It is assumed that the first "Voronezh-VP" will be deployed in the city of Olenegorsk in the Kola Peninsula (n. N. The ducts) by the end of 2018 and will replace the radar "Dnepr", properly functioning there for decades. Power consumption of modern radar around 10 MW. Compared to previous versions of "Voronezh" it will increase the number of transceivers blocks.
Perspective radar "Voronezh-SM", exist only in draft, will work in the centimeter range.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
https://www.shephardmedia.com/news/imps ... -new-mcmv/
WE cearlier operated similar cinshore MCVs of the Yevgenya class.Russian Navy takes delivery of MCMV
07th January 2017 - 12:00 by Alex Mladenov & Krassimir Grozev in Sofia
Russian Navy takes delivery of MCMV
The Russian Navy last month finally received the first of a new-generation of mine hunters at a ceremony in St Petersburg, the lead ship of the Project 12700 vessels destined for service.
In a ceremony at the Baltic Fleet Naval base in Kronshtadt on 9 December the newly-commissioned vessel, named the Alexander Obukhov, represents a indication of Russia's continued efforts to improve its maritime capabilities.
Project 12700 mine hunters are mainly intended for mine countermeasures operations in the close proximity of naval bases and littoral areas. Designed by Almaz in St Petersburg, the ships are built at the Sredno-Dnevsky Shipyard in the same city.
The production however proved to be a long-delayed process, as the Alexander Obukhov was laid down in September 2007, but launch reportedly only occurring in June 2014. The completion of build activities has taken another two years.
Another ship of the same class currently in production, in addition to a contract for five additional vessels, which are scheduled for delivery by the end of 2021. The Indian Navy has also expressed interest in procuring ships of the same class and is expected to look closely at the initial operations of the Alexander Obukhov.
The vessels hull has been fabricated from non-metallic materials with the manufacturer claiming it to be the largest hull built as a mono-assembly from fiberglass using the vacuum infusion. Its displacement is 900t, with a length of 61.75m.
The maximum speed is 17kt while an economic speed of 10kt enables a range of up to 1,500nm. The autonomy is 10 days. Armament consists of a 30mm AK-306 gun and a single 14.5mm machine gun. The complement is around 40 officers and personnel.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
looking at the fit and finish of the russian aircraft, are the fabled "noise & pollution regulations" that keep ilyushin and antonov out of the american-EU market sales a political play to protect airbus and boeing or really a environmental issue ?
the big one with 4 engines looks exactly like a 777200LR with 4 engines
the big one with 4 engines looks exactly like a 777200LR with 4 engines
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
4 engine makes it Higher Fuel Consumption compared to modern Western Peers which are twin engine ,Il-96 was made at time SU collapsed so next 10 years they did not developed it by then Wide Body Aircraft moved towards twin engine type like 777/787/350 typesSingha wrote:looking at the fit and finish of the russian aircraft, are the fabled "noise & pollution regulations" that keep ilyushin and antonov out of the american-EU market sales a political play to protect airbus and boeing or really a environmental issue ?
Now they are making Il-96-400M a stretched version of IL-96-300 that you see in picture re-engining with modern PD-14M that would make its operational cost comparable to 777-200 and A-330-300 ....This is for their domestic long haul ,large passenger ( 400 pax ) low cost carrier.
http://bisnisinsight.com/ilyushin-il-96 ... -the-west/
The Wide body aircraft joiintly developing with Chinese would be comparable to its more modern western counterpart 787/350
Roughly not exactly the 777 are more bigger but the stretched IL-96-400M would be comparable to 777-200the big one with 4 engines looks exactly like a 777200LR with 4 engines
The Tu-204/214 are comparable to 757 narrow body jets
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russian Heavy/Medium/Light UCAV/UAV program ( via Pralay )
1 ) Company Sukhoi + MiG = "Охотник / Hunter," take-off weight of 20 tons, attack, the first flight of 2018. Analogue of the X-47B
Patient filed by Mig http://bd.patent.su/2353000-2353999/pat ... t3c0b.html
http://bd.patent.su/2353000-2353999/ima ... 353547.tif
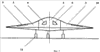
2 ) Company Irkut aviation plant + Yak = "Прорыв / Breakthrough" (Yak-133), take-off weight of 10 tons, attack, first flight in September 2016.

3 ) Company "Simonov" + Kazan aviation plant = "Альтаир / Altair", take-off weight of 5 tons,Survellence scout

4 ) Company Myasischev + TsAGI = "Обзор-1 / Review-1", first flight 2017, analogue Global Hawk

5 ) Company "Kronstadt" = ..., take-off weight of 1.2 tons, scout / attack. Analogue Predator
1 ) Company Sukhoi + MiG = "Охотник / Hunter," take-off weight of 20 tons, attack, the first flight of 2018. Analogue of the X-47B
Patient filed by Mig http://bd.patent.su/2353000-2353999/pat ... t3c0b.html
http://bd.patent.su/2353000-2353999/ima ... 353547.tif

2 ) Company Irkut aviation plant + Yak = "Прорыв / Breakthrough" (Yak-133), take-off weight of 10 tons, attack, first flight in September 2016.

3 ) Company "Simonov" + Kazan aviation plant = "Альтаир / Altair", take-off weight of 5 tons,Survellence scout

4 ) Company Myasischev + TsAGI = "Обзор-1 / Review-1", first flight 2017, analogue Global Hawk

5 ) Company "Kronstadt" = ..., take-off weight of 1.2 tons, scout / attack. Analogue Predator
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
AD exercise modernised Strela-MN , Tor-2K
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russia allows military spare-parts makers to deal with India directly - this should help in improving availability of critical spares for us
http://www.tribuneindia.com/news/nation ... 49283.html
http://www.tribuneindia.com/news/nation ... 49283.html
In a major development, Russia has allowed its military spare parts manufacturers to sell items directly to India. This will improve servicing and repairs of Russian/Soviet-origin equipment.
About 70 per cent of military equipment with the Indian armed forces — the Army, Indian Air Force and the Navy — is from Russia. With Moscow continuing to be the largest supplier of military hardware, this scenario will not change for the next three decades.
Repairs and servicing of key equipment is hampered by lack of ready availability of spares and a rather circuitous route through a single agency in Moscow makes it even more lengthy. The Russian permission will help, among other aspects, in improving the servicing and repair of the Sukhoi-30 MKI fighter jets, the Mi-17 helicopters, Navy warships and T-90 tanks.
The Russian Ministry of Defence has conveyed the decision to their Indian counterparts through an official communication. “The communiqué from Russia details which all companies or original equipment manufacturers have been permitted to sell spare parts to India directly without seeking permission for each tranche,” a source in the MoD confirmed. The MoD here has further circulated the list of companies permitted by Moscow to the three services asking them to see and check if any company which deals with India has been left out. The matter has been discussed during the summit meeting between PM Narendra Modi and Russian President Vladimir Putin last year.
A senior functionary said the Russian manufacturers of military equipment source key parts, such as engines, avionics, weaponry from producers within Russia and sometimes even Ukraine to integrate them on planes or warships or tanks.
All military equipment by the very nature of it needs consumable parts which have ‘run-life’ and need to be changed or overhauled after its specified life. For example, the engine of the Sukhoi-30 needs to be overhauled after 800-900 hours of flying.
The Sukhoi is serviced and maintained by the PSU Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL). There are four key suppliers. The Sukhoi has an availability rate of 65 per cent and large parts of it due to delay in spares. The IAF’s operated base repair depots maintain the fleet of Mi-17s while the Navy maintains its own warships at naval dockyards. Sources here said once this is done, HAL, IAF, Navy and the Army can source spares from Russia.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Putin's concentration upon the Russian navy's sub fleet modernisation over the last decade is paying off. The two new classes of Borei and Yasen SSBN/SSGN are now being built in upgraded variants. Another smaller SSN is also on the cards ,Kilo and Amur/Lada class subs being churned out like sausages,with the new Kalina class awaited as well.Add to this the extensive revamping of older Sov. era N-boats ,adding a few more decades of life to those valuable subs.By 2020 the RuN's sub fleet will have both quality and quantity to be envied by any superpower or aspiring superpower.NATO will be in "deep sh*t",pardon the pun,and the stupid Brits,who pensioned off in indecent haste their superb Nimrod LRMP aircraft and Harriers ,will be up the Loch without a paddle,and the woes of Brexit weighing heavily upon its defence budget.
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2017/01 ... ays-first/
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2017/01 ... ays-first/
Navy facing heaviest Russian activity since Cold War says First Sea Lord
The frigate HMS Kent shadowing the Russian submarine Stary Osko
Ben Farmer, Defence Correspondent
15 January 2017 • 10:00pm
The Royal Navy is facing its greatest challenge from Russian submarines and warships for more than 25 years, the First Sea Lord has told his sailors.
Adml Sir Philip Jones said the Navy was dealing with the highest level of activity from Vladimir Putin’s fleet since the end of the Cold War, even as it has to make “difficult” cuts to equipment.
The message from the head of the Royal Navy comes as British warships are again being readied to escort the Russian carrier Admiral Kuznetsov past the UK as it returns from its bombing campaign against Syrian rebels.
A handout photograph made available by Dover Marina.com on 21 October 2016 showing Russian aircraft carrier Admiral Kuznetsov in the English Channel, 21 October 2016.
The Admiral Kuznetsov is due to be escorted past the UK again in the coming weeks as it returns from the Mediterranean Credit: Dover Marina/Handout
But naval sources said high profile deployments by Russia’s surface fleet were of far less concern than a sharp increase in Russian submarine missions in waters north of Scotland.
British frigates and submarines, backed by Nato allies, are waging an increasingly intense cat and mouse game trying to find and track the Russian vessels.
Russia analysts fear the jump in submarine activity to levels not seen since the 1980s is accompanied by increased efforts to spy on Britain’s nuclear deterrent vessels, based at Faslane.
In a New Year message to the Navy, Sir Philip said: “In northern Europe and the Baltic, we are responding to the highest level of Russian naval activity since the end of the Cold War.”
Russian President Vladimir Putin greets military officers during a promotion ceremony at the Kremlin Russian President Vladimir Putin during duties, Moscow, Russia
Vladimir Putin has poured money into the Russian military and radically modernised his fleet
His comments follow a warning last year by the commander of the US Navy’s European fleet that Nato was on the verge of a new “battle of the Atlantic” with increasingly sophisticated Russian submarines.
Dr Andrew Foxall, director of the Russia Studies Centre at the Henry Jackson Society, said waters separating Greenland, Iceland and the UK which had once been a key Cold War battleground were again the centre of a secret confrontation.
The so-called GIUK gap represents the gateway for Russian vessels entering the Atlantic and during the Cold War was one of the most watched stretches of water in the world.
Watch | US Navy releases new video of Russian fighters 'buzzing' destroyer
01:03
He said: “I don’t think it’s the increase in absolute number [of missions] that’s the increase of concern, it’s the information that these Russian submarines are trying to collect.”
“Russia has been ramping up its presence in the North Atlantic at the same time that other countries have been winding there’s down.”
He said the UK decision to scrap the troubled Nimrod maritime surveillance aircraft in 2010 and the delay in getting the Boeing P8 replacement had “left the country vulnerable to the sort of activity that Russian submarines conduct”.
Sir Philip also admitted the Royal Navy is battling budget, manning and equipment woes after details of cuts and personnel shortfalls were revealed. The Navy is understood to be facing a £500m budget black hole with commanders ordered to find more savings.
Writing in Navy News, he said the power plants of the Type 45 destroyers, which are to have engine refits after a string of power failures, “have turned out to be less reliable than originally envisaged”.
But he said the difficulties were “the challenges of a first rate Navy”. He said: “You don’t hear about the same issues in many other navies – and believe me, they exist – because they don’t operate with the same sophistication or expectation.”
A Royal Navy frigate and destroyer are on standby to accompany the Kuznetsov when it passes back past the UK in the coming weeks. The ageing carrier is currently in the Mediterranean accompanied by a Russian battlecruiser, two destroyers and a tanker.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Russian tents for -40 C
http://englishrussia.com/2017/01/17/fir ... reme-40-c/
excellent tent setup, go through all pics
http://englishrussia.com/2017/01/17/fir ... reme-40-c/
excellent tent setup, go through all pics
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Old report,but v.interesting details.The IN has to one's knowledge no research/trials subs since our Foxtrots were retired.
http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2 ... arine.html
http://www.thedailybeast.com/articles/2 ... arine.html
RED OCTOBER REDUX?
Russia’s Mysterious New Submarine
It looks like the Moscow vs. the USS Jimmy Carter. But can the Kremlin afford the ship’s new technology?
DAVID AXE
08.21.15 10:30 AM ET
On August 11 at the port of Severodvinsk in northern Russia, a huge and imposing black shape emerged from a dry dock, observed by ranks of uniformed dignitaries. The Russian navy’s latest submarine is 574 feet long, displaces no fewer than 18,000 tons of water and packs two nuclear reactors.
Named Moscow, she’s actually a refurbished, 1980s-vintage ballistic-missile sub that once prowled underneath the Arctic ice, cradling nuclear-tipped ballistic missiles, awaiting Armageddon.
Today, as best as any outside observer can tell, the Moscow has a new mission. She appears to be part science vessel, part spy ship, part commando transport, and part “mothership” for mini-subs and drones.
But no one outside of the Kremlin and the Moscow’s future crew knows for sure.
“There’s a lot of questions here,” says Eric Wertheim, a leading naval analyst in the United States and author of Combat Fleets of the World, the definitive naval reference guide.
One thing is certain: Whatever her purpose, the Moscow is the most recent sign of Russia’s desperate effort to rebuild its dilapidated navy and, a quarter-century after the Cold War ended, once again challenge the U.S. Navy on—and beneath—the world’s oceans.
Special mission boat
Moscow began life as a Delta IV-class ballistic missile submarine, crewed by 135 sailors and armed with 16 intercontinental-range ballistic missiles, each with four independent warheads that can split off from the rocket as it plummets toward Earth, maximizing the city-destroying power of each missile.
In 1999, the Kremlin ordered the Moscow into dry dock in Severodvinsk for rework initially costing 443 million rubles, or around $7 million. The plan—to remove the submarine’s missile tubes and replace them with new equipment for covert missions, transforming the Moscow into what navies call a “special mission” vessel.
Where ballistic missile subs haul atomic weapons and so-called attack submarines armed with non-nuclear missiles and torpedoes silently stalk surface ships and other subs, special-mission boats handle, well, everything else that an undersea warship can do: testing new technology; quietly transporting naval commandos on deadly secret missions; supporting deep-diving mini-submarines and free-swimming underwater robots; and, perhaps most provocatively, gathering intelligence—and preventing the enemy’s submarines from collecting intel of their own.
The United States is the world’s leader in submarine technology and possesses the most technologically advanced special-mission subs, including four converted ballistic-missile submarines plus the mysterious USS Jimmy Carter, a one-of-a-kind spin-off of the Seawolf class of attack boats.
Entering service in 2004, the $3 billion Jimmy Carter is one of the Navy’s most secretive warships. The sailing branch does not comment on the vessel’s features and deployments. But Owen Cote, a submarine expert at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, said the ship probably has a “moon well,” a kind of floodable chamber that allows divers and undersea drones to exit and reenter the sub while the ship is submerged.
It’s unclear exactly what the Jimmy Carter does during her months-long deployments, but it’s possible she heads to the ocean floor so her divers and robots can place wiretaps on undersea cables, allowing U.S. intelligence agencies to listen in on intercontinental communications including Internet traffic. During the Cold War, U.S. special mission subs frequently penetrated Soviet defenses to bug Moscow’s communications cables.
These days there are better ways to tap into the fiber-optic cables that carry global communications. “I don’t think you need to use Jimmy Carter to do that,” Cote said. “It would be a waste of that asset.”
But one Russian ex-official insists that NATO, the U.S.-led European military alliance, still taps Moscow’s cables. “I note that every year a certain number of such devices is removed from our links,” retired admiral Viktor Kravchenko, former chief of the general staff of the Russian navy, told one Russian news site.
Indeed, Kravchenko claimed that the Moscow’s main mission will be to transport a nuclear-powered mini-sub that can descend to great depths to remove the wiretaps. The Moscow’s mini-sub could also place its own wiretaps, according to Valentin Selivanov, another retired Russian admiral and former submarine commander.
Like Cote, Norman Polmar—a naval expert who has advised the U.S. government on submarine strategy—dismissed all this talk of wiretaps. “There are very few Russian undersea cables that are tappable,” Polmar said. Besides, he added, “more stuff moves through the air.”
Cash is king
Still, Polmar cautioned against underestimating the Moscow. Whatever the submarine is for, it could be something American observers can’t even imagine. “Is there something surprisng in that submarine?” Polmar asked. “It’s possible.”
Polmar said he has visited, multiple times, all of the engineering bureaus that design Russia’s subs. “These guys are far more innovative than we ever were.”
But before the Moscow can take on secret missions, the Kremlin has to wrap up the submarine’s rework—a process that, so far, has taken a staggering 16 years… and might never get finished.
Russia’s naval shipbuilding industry still possesses impressive expertise, but has suffered from inconsistent and inadequate government funding ever since the Cold War ended. From a peak of hundreds of undersea vessels during the Soviet era, today the Russian navy can put to sea just a couple dozen submarines, roughly half as many as the better-funded U.S. Navy can manage.
“The trouble with all these naval issues is that, unlike some programs that are small, ships are systems of systems and require stable funding over a long period of time,” Wertheim said. And stability is the one thing the Russian economy—and by extension the country’s military budgets—definitely lack.
The Moscow left dry dock on August 12 but could still be years away from being combat-ready. A photo of her relaunch shows construction scaffolding on top of her hull. But Wertheim said he expects the Kremlin to push hard to complete the sub, despite the challenges. “They don’t want to lose that intelligence-collection capability.”
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
philip: as much as possible, please do not post entire articles from links. Title and link is sufficient. Copyright laws are fairly stringent now. If you want to make a point, quote a portion of the article. But nothing more.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
Will do where Cright rules prevail.Tx.
Is thia Russia's deadliest "weapon"? ASk Putin!
Vladimir Putin: 'Our prostitutes are the best in the world, but I doubt Donald Trump would fall for them'
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2017/01 ... -swindler/
Is thia Russia's deadliest "weapon"? ASk Putin!
Vladimir Putin: 'Our prostitutes are the best in the world, but I doubt Donald Trump would fall for them'
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2017/01 ... -swindler/
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
2016 Kubinka Tu-95 Tu-160 Tu-22 takeoff
-
Manish_Sharma
- BRF Oldie
- Posts: 5128
- Joined: 07 Sep 2009 16:17
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
are these new torpedoes or old shakvals?Philip wrote:https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/che ... h-in-2017/The Yasen, according to Spahn’s piece, has eight torpedo tubes, capable of launching underwater projectiles that can reach roughly 230 mph.
Re: Russian weapons and military technology
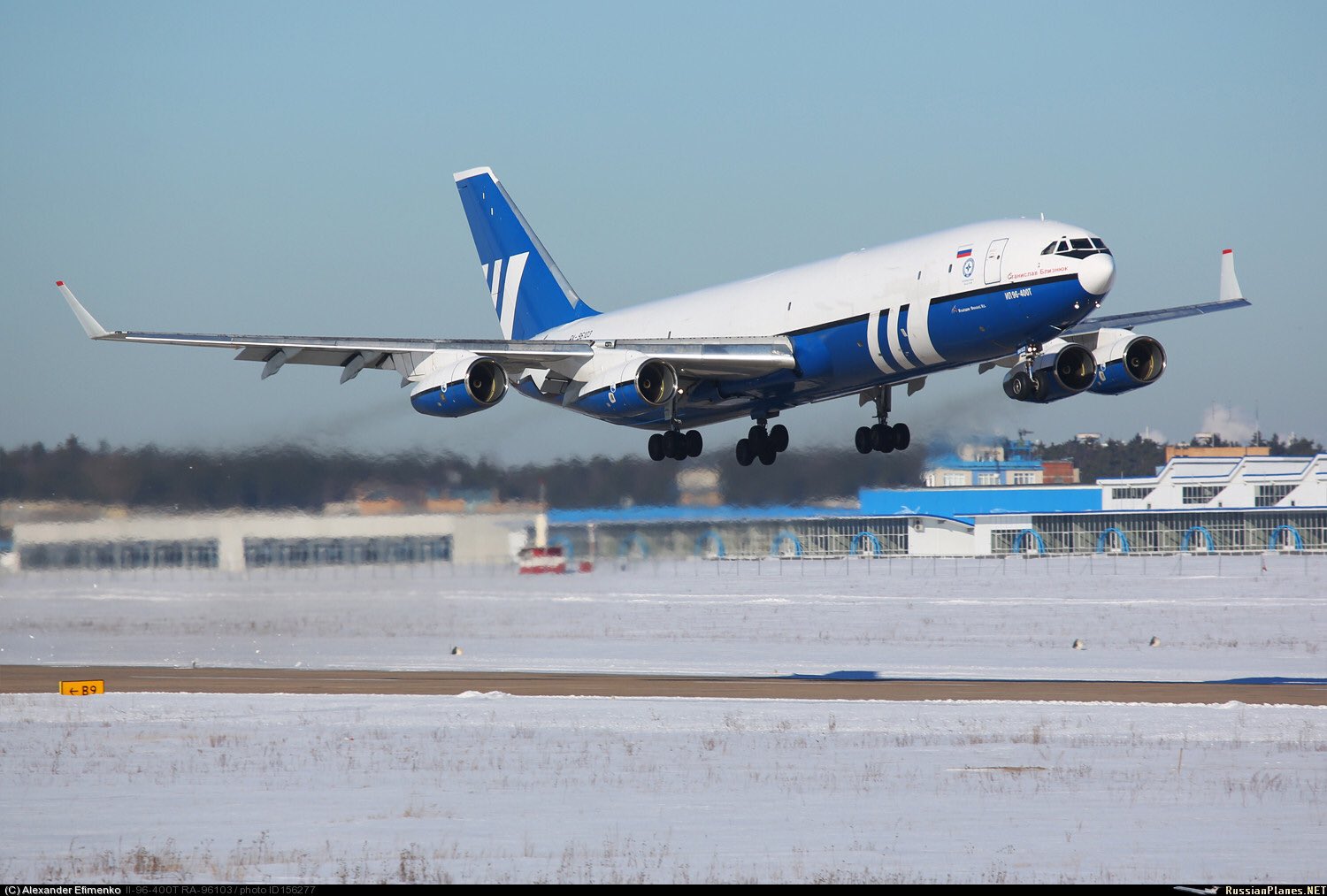


Rus successfully conducted joint flying tests of Il-96-400T & RuAF fighters as stage to develop strategic air tanker on base of Il-96-
Il-96-400TZ strategic air tanker to be able to refuel: - 65 t at distance of 3500 km or - 35 t at / 7300 km
https://twitter.com/RSS_40